Blog Archives
Beyond the Buzz: The Real Economics Behind SaaS, AI, and Everything in Between
Posted by Hindol Datta
Introduction
Throughout my career, I have had the privilege of working in and leading finance teams across several SaaS companies. The SaaS model is familiar territory to me: its economics are well understood, its metrics are measurable, and its value creation pathways have been tested over time. Erich Mersch’s book on SaaS Hacks is my Bible. In contrast, my exposure to pure AI companies has been more limited. I have directly supported two AI-driven businesses, and much of my perspective comes from observation, benchmarking, and research. This combination of direct experience and external study has hopefully shaped a balanced view: one grounded in practicality yet open to the new dynamics emerging in the AI era.

Across both models, one principle remains constant: a business is only as strong as its unit economics. When leaders understand the economics of their business, they gain the ability to map them to daily operations, and from there, to the financial model. The linkage from unit economics to operations to financial statements is what turns financial insight into strategic control. It ensures that decisions on pricing, product design, and investment are all anchored in how value is truly created and captured.
Today, CFOs and CEOs must not only manage their profit and loss (P&L) statement but also understand the anatomy of revenue, cost, and cash flow at the micro level. SaaS, AI, and hybrid SaaS-AI models each have unique economic signatures. SaaS rewards scalability and predictability. AI introduces variability and infrastructure intensity. Hybrids offer both opportunity and complexity. This article examines the financial structure, gross margin profile, and investor lens of each model to help finance leaders not only measure performance but also interpret it by turning data into judgment and judgment into a better strategy.
Part I: SaaS Companies — Economics, Margins, and Investor Lens
The heart of any SaaS business is its recurring revenue model. Unlike traditional software, where revenue is recognized upfront, SaaS companies earn revenue over time as customers subscribe to a service. This shift from ownership to access creates predictable revenue streams but also introduces delayed payback cycles and continuous obligations to deliver value. Understanding the unit economics behind this model is essential for CFOs and CEOs, as it enables them to see beyond top-line growth and assess whether each customer, contract, or cohort truly creates long-term value.
A strong SaaS company operates like a flywheel. Customer acquisition drives recurring revenue, which funds continued innovation and improved service, in turn driving more customer retention and referrals. But a flywheel is only as strong as its components. The economics of SaaS can be boiled down to a handful of measurable levers: gross margin, customer acquisition cost, retention rate, lifetime value, and cash efficiency. Each one tells a story about how the company converts growth into profit.
The SaaS Revenue Engine
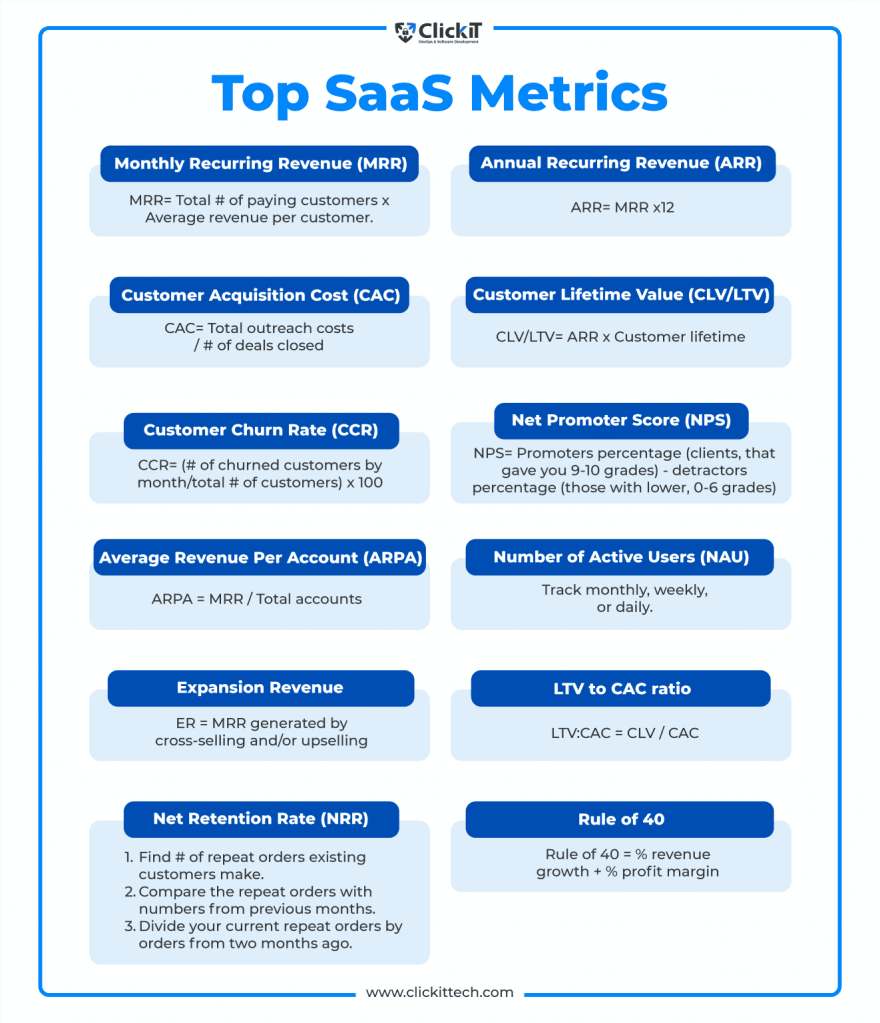
At its simplest, a SaaS company makes money by providing access to its platform on a subscription basis. The standard measure of health is Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR). ARR represents the contracted annualized value of active subscriptions. It is the lifeblood metric of the business. When ARR grows steadily with low churn, the company can project future cash flows with confidence.
Revenue recognition in SaaS is governed by time. Even if a customer pays upfront, the revenue is recognized over the duration of the contract. This creates timing differences between bookings, billings, and revenue. CFOs must track all three to understand both liquidity and profitability. Bookings signal demand, billings signal cash inflow, and revenue reflects the value earned.
One of the most significant advantages of SaaS is predictability. High renewal rates lead to stable revenues. Upsells and cross-sells increase customer lifetime value. However, predictability can also mask underlying inefficiencies. A SaaS business can grow fast and still destroy value if each new customer costs more to acquire than they bring in lifetime revenue. This is where unit economics comes into play.
Core Unit Metrics in SaaS
The three central metrics every CFO and CEO must know are:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total sales and marketing expenses needed to acquire one new customer.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): The total revenue a customer is expected to generate over their relationship with the company.
- Payback Period: The time it takes for gross profit from a customer to recover CAC.
A healthy SaaS business typically maintains an LTV-to-CAC ratio of at least 3:1. This means that for every dollar spent acquiring a customer, the company earns three dollars in lifetime value. Payback periods under twelve months are typically considered strong, especially in mid-market or enterprise SaaS. Long payback periods signal cash inefficiency and high-risk during downturns.
Retention is equally essential. The stickier the product, the lower the churn, and the more predictable the revenue. Net revenue retention (NRR) is a powerful metric because it combines churn and expansion. A business with 120 percent NRR is growing revenue even without adding new customers, which investors love to see.
Gross Margin Dynamics
Gross margin is the backbone of SaaS profitability. It measures how much of each revenue dollar remains after deducting direct costs, such as hosting, support, and third-party software fees. Well-run SaaS companies typically achieve gross margins of between 75% and 85%. This reflects the fact that software is highly scalable. Once built, it can be replicated at almost no additional cost. They use the margins to fund their GTM strategy. They have room until they don’t.
However, gross margin is not guaranteed. In practice, it can erode for several reasons. First, rising cloud infrastructure costs can quietly eat into margins if not carefully managed. Companies that rely heavily on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud need cost optimization strategies, including reserved instances and workload tuning. Second, customer support and success functions, while essential, can become heavy if processes are not automated. Third, complex integrations or data-heavy products can increase variable costs per customer.
Freemium and low-entry pricing models can also dilute margins if too many users remain on free tiers or lower-paying plans. The CFO’s job is to ensure that pricing reflects the actual value delivered and that the cost-to-serve remains aligned with revenue per user. A mature SaaS company tracks unit margins by customer segment to identify where profitability thrives or erodes.
Operating Leverage and the Rule of 40
The power of SaaS lies in its potential for operating leverage. Fixed costs, such as R&D, engineering, and sales infrastructure, remain relatively constant as revenue scales. As a result, incremental revenue flows disproportionately to the bottom line once the business passes break-even. This makes SaaS an attractive model once scale is achieved, although reaching that scale can take a considerable amount of time.
The Rule of 40 is a shorthand metric many investors use to gauge the balance between growth and profitability. It states that a SaaS company’s revenue growth rate, plus its EBITDA margin, should equal or exceed 40 percent. A company growing 30 percent annually with a 15 percent EBITDA margin scores 45, which is considered healthy. A company growing at 60 percent but losing 30 percent EBITDA would score 30, suggesting inefficiency. This rule forces management to strike a balance between ambition and discipline. This 40% rule was based on empirical analysis, and every Jack and Jill swears by it. I am not sure that we can have this Rule and apply it blindly. I am not generally in favor of these broad rules. That is a lot of fodder for a different conversation.
Cash Flow and Efficiency
Cash flow timing is another defining feature of SaaS. Many customers prepay annually, creating favorable working capital dynamics. This gives SaaS companies negative net working capital, which can help fund growth. However, high upfront CAC and long payback periods can strain cash reserves. CFOs must ensure growth is financed efficiently and that burn multiples remain sustainable. Burn-multiple measures the cash burn relative to net new ARR added. A burn rate of multiple below 1 is excellent; it means the company spends one dollar to generate one dollar of recurring revenue. Ratios above 2 suggest inefficiency.
As markets have tightened, investors have shifted focus from pure growth to efficient growth. Cash is no longer cheap, and dilution from equity raises is costly. I attended a networking event in San Jose about a month ago, and one of the finance leaders said, “We are in the middle of a nuclear winter.” I thought that summarized the current state of the funding market. Therefore, SaaS CFOs must guide companies toward self-funding growth, improving gross margins, and shortening CAC payback cycles.
Valuation and Investor Perspective
Investors view SaaS companies through the lens of predictability, scalability, and margin potential. Historically, during low-interest-rate periods, high-growth SaaS companies traded at 10 to 15 times ARR. In the current normalized environment, top performers trade between 5 and 8 times ARR, with discounts for slower growth or lower margins.
The key drivers of valuation include:
- Growth Rate: Faster ARR growth leads to higher multiples, provided it is efficient.
- Gross Margin: High margins indicate scalability and control over cost structure.
- Retention and Expansion: Strong NRR signals durable revenue and pricing power.
- Profitability Trajectory: Investors reward companies that balance growth with clear paths to cash flow breakeven.
Investors now differentiate between the quality of growth and the quantity of growth. Revenue driven by deep discounts or heavy incentives is less valuable than revenue driven by customer adoption and satisfaction. CFOs must clearly communicate cohort performance, renewal trends, and contribution margins to demonstrate that growth is sustainable and durable.
Emerging Challenges in SaaS Economics
While SaaS remains a powerful model, new challenges have emerged. Cloud infrastructure costs are rising, putting pressure on gross margins. AI features are becoming table stakes, but they introduce new variable costs tied to compute. Customer expectations are also shifting toward usage-based pricing, which can lead to reduced predictability in revenue recognition.
To navigate these shifts, CFOs must evolve their financial reporting and pricing strategies. Gross margin analysis must now include compute efficiency metrics. Sales compensation plans must reflect profitability, not just bookings. Pricing teams must test elasticity to ensure ARPU growth outpaces cost increases.
SaaS CFOs must also deepen their understanding of cohort economics. Not all customers are equal. Some segments deliver faster payback and higher retention, while others create drag. Segmented reporting enables management to allocate capital wisely and avoid pursuing unprofitable markets.
The Path Forward
The essence of SaaS unit economics is discipline. Growth only creates value when each unit of growth strengthens the financial foundation. This requires continuous monitoring of margins, CAC, retention, and payback. It also requires cross-functional collaboration between finance, product, and operations. Finance must not only report outcomes but also shape strategy, ensuring that pricing aligns with value and product decisions reflect cost realities.
For CEOs, understanding these dynamics is vital to setting priorities. For CFOs, the task is to build a transparent model that links operational levers to financial outcomes. Investors reward companies that can tell a clear story with data: a path from top-line growth to sustainable free cash flow.
Ultimately, SaaS remains one of the most attractive business models when executed effectively. The combination of recurring revenue, high margins, and operating leverage creates long-term compounding value. But it rewards precision. The CFO who masters unit economics can turn growth into wealth, while the one who ignores it may find that scale without discipline is simply a faster road to inefficiency. The king is not dead: Long live the king.
Part II: Pure AI Companies — Economics, Margins, and Investor Lens
Artificial intelligence companies represent a fundamentally different business model from traditional SaaS. Where SaaS companies monetize access to pre-built software, AI companies monetize intelligence: the ability of models to learn, predict, and generate. This shift changes everything about unit economics. The cost per unit of value is no longer near zero. It is tied to the underlying cost of computation, data processing, and model maintenance. As a result, CFOs and CEOs leading AI-first companies must rethink what scale, margin, and profitability truly mean.
While SaaS scales easily once software is built, AI scales conditionally. Each customer interaction may trigger new inference requests, consume GPU time, and incur variable costs. Every additional unit of demand brings incremental expenses. The CFO’s challenge is to translate these technical realities into financial discipline, which involves building an organization that can sustain growth without being constrained by its own cost structure.
Understanding the AI Business Model
AI-native companies generate revenue by providing intelligence as a service. Their offerings typically fall into three categories:
- Platform APIs: Selling access to models that perform tasks such as image recognition, text generation, or speech processing.
- Enterprise Solutions: Custom model deployments tailored for specific industries like healthcare, finance, or retail.
- Consumer Applications: AI-powered tools like copilots, assistants, or creative generators.
Each model has unique economics. API-based businesses often employ usage-based pricing, resembling utilities. Enterprise AI firms resemble consulting hybrids, blending software with services. Consumer AI apps focus on scale, requiring low-cost inference to remain profitable.
Unlike SaaS subscriptions, AI revenue is often usage-driven. This makes it more elastic but less predictable. When customers consume more tokens, queries, or inferences, revenue rises but so do costs. This tight coupling between revenue and cost means margins depend heavily on technical efficiency. CFOs must treat cost-per-inference as a central KPI, just as SaaS leaders track gross margin percentage.
Gross Margins and Cost Structures
For pure AI companies, the gross margin reflects the efficiency of their infrastructure. In the early stages, margins often range between 40% and 60%. With optimization, some mature players approach 70 percent or higher. However, achieving SaaS-like margins requires significant investment in optimization techniques, such as model compression, caching, and hardware acceleration.
The key cost components include:
- Compute: GPU and cloud infrastructure costs are the most significant variable expenses. Each inference consumes compute cycles, and large models require expensive hardware.
- Data: Training and fine-tuning models involve significant data acquisition, labeling, and storage costs.
- Serving Infrastructure: Orchestration, latency management, and load balancing add further expenses.
- Personnel: Machine learning engineers, data scientists, and research teams represent high fixed costs.
Unlike SaaS, where the marginal cost per user declines toward zero, AI marginal costs can remain flat or even rise with increasing complexity. The more sophisticated the model, the more expensive it is to serve each request. CFOs must therefore design pricing strategies that match the cost-to-serve, ensuring unit economics remain positive.
To track progress, leading AI finance teams adopt new metrics such as cost per 1,000 tokens, cost per inference, or cost per output. These become the foundation for gross margin improvement programs. Without these metrics, management cannot distinguish between profitable and loss-making usage.
Capital Intensity and Model Training
A defining feature of AI economics is capital intensity. Training large models can cost tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. These are not operating expenses in the traditional sense; they are long-term investments. The question for CFOs is how to treat them. Should they be expensed, like research and development, or capitalized, like long-lived assets? The answer depends on accounting standards and the potential for model reuse.
If a model will serve as a foundation for multiple products or customers over several years, partial capitalization may be a defensible approach. However, accounting conservatism often favors expensing, which depresses near-term profits. Regardless of treatment, management must view training costs as sunk investments that must earn a return through widespread reuse.
Due to these high upfront costs, AI firms must carefully plan their capital allocation. Not every model warrants training from scratch. Fine-tuning open-source or pre-trained models may achieve similar outcomes at a fraction of the cost. The CFO’s role is to evaluate return on invested capital in R&D and ensure technical ambition aligns with commercial opportunity.
Cash Flow Dynamics
Cash flow management in AI businesses is a significant challenge. Revenue often scales more slowly than costs in early phases. Infrastructure bills accrue monthly, while customers may still be in pilot stages. This results in negative contribution margins and high burn rates. Without discipline, rapid scaling can amplify losses.
The path to positive unit economics comes from optimization. Model compression, quantization, and batching can lower the cost per inference. Strategic use of lower-cost hardware, such as CPUs for lighter tasks, can also be beneficial. Some firms pursue vertical integration, building proprietary chips or partnering for preferential GPU pricing. Others use caching and heuristic layers to reduce the number of repeated inference calls.
Cash efficiency improves as AI companies move from experimentation to productization. Once a model stabilizes and workload patterns become predictable, cost forecasting and margin planning become more reliable. CFOs must carefully time their fundraising and growth, ensuring the company does not overbuild infrastructure before demand materializes.
Pricing Strategies
AI pricing remains an evolving art. Standard models include pay-per-use, subscription tiers with usage caps, or hybrid pricing that blends base access fees with variable usage charges. The proper structure depends on the predictability of usage, customer willingness to pay, and cost volatility.
Usage-based pricing aligns revenue with cost but increases forecasting uncertainty. Subscription pricing provides stability but can lead to margin compression if usage spikes. CFOs often employ blended approaches, utilizing base subscriptions that cover average usage, with additional fees for exceeding demand. This provides a buffer against runaway costs while maintaining customer flexibility.
Transparent pricing is crucial. Customers need clarity about what drives cost. Complexity breeds disputes and churn. Finance leaders should collaborate with product and sales teams to develop pricing models that are straightforward, equitable, and profitable. Scenario modeling helps anticipate edge cases where heavy usage erodes margins.
Valuation and Investor Perspective
Investors evaluate AI companies through a different lens than SaaS. Because AI is still an emerging field, investors look beyond current profitability and focus on technical moats, data advantages, and the scalability of cost curves. A strong AI company demonstrates three things:
- Proprietary Model or Data: Access to unique data sets or model architectures that competitors cannot easily replicate.
- Cost Curve Mastery: A clear path to reducing cost per inference as scale grows.
- Market Pull: Evidence of real-world demand and willingness to pay for intelligence-driven outcomes.
Valuations often blend software multiples with hardware-like considerations. Early AI firms may be valued at 6 to 10 times forward revenue if they show strong growth and clear cost reduction plans. Companies perceived as purely research-driven, without commercial traction, face steeper discounts. Investors are increasingly skeptical of hype and now seek proof of sustainable margins.
In diligence, investors focus on gross margin trajectory, data defensibility, and customer concentration. They ask questions like: How fast is the cost per inference declining? What portion of revenue comes from repeat customers? How dependent is the business on third-party models or infrastructure? The CFO’s job is to prepare crisp, data-backed answers.
Measuring Efficiency and Scale
AI CFOs must introduce new forms of cost accounting. Traditional SaaS dashboards that focus solely on ARR and churn are insufficient. AI demands metrics that link compute usage to financial outcomes. Examples include:
- Compute Utilization Rate: Percentage of GPU capacity effectively used.
- Model Reuse Ratio: Number of applications or customers served by a single trained model.
- Cost per Output Unit: Expense per generated item, prediction, or token.
By tying these technical metrics to revenue and gross margin, CFOs can guide engineering priorities. Finance becomes a strategic partner in improving efficiency, not just reporting cost overruns. In a later article, we will discuss complexity and Scale. I am writing a book on that subject, and this is highly relevant to how AI-based businesses are evolving. It is expected to be released by late February next year and will be available on Kindle as an e-book.
Risk Management and Uncertainty
AI companies face unique risks. Dependence on external cloud providers introduces pricing and supply risks. Regulatory scrutiny over data usage can limit access to models or increase compliance costs. Rapid technological shifts may render models obsolete before their amortization is complete. CFOs must build contingency plans, diversify infrastructure partners, and maintain agile capital allocation processes.
Scenario planning is essential. CFOs should model high, medium, and low usage cases with corresponding cost structures. Sensitivity analysis on cloud pricing, GPU availability, and demand elasticity helps avoid surprises. Resilience matters as much as growth.
The Path Forward
For AI companies, the journey to sustainable economics is one of learning curves. Every technical improvement that reduces the cost per unit enhances the margin. Every dataset that improves model accuracy also enhances customer retention. Over time, these compounding efficiencies create leverage like SaaS, but the path is steeper.
CFOs must view AI as a cost-compression opportunity. The winners will not simply have the best models but the most efficient ones. Investors will increasingly value businesses that show declining cost curves, strong data moats, and precise product-market fit.
For CEOs, the message is focus. Building every model from scratch or chasing every vertical can drain capital. The best AI firms choose their battles wisely, investing deeply in one or two defensible areas. Finance leaders play a crucial role in guiding these choices with evidence, rather than emotion.
In summary, pure AI companies operate in a world where scale is earned, not assumed. The economics are challenging but not insurmountable. With disciplined pricing, rigorous cost tracking, and clear communication to investors, AI businesses can evolve from capital-intensive experiments into enduring, high-margin enterprises. The key is turning intelligence into economics and tackling it one inference at a time.
Part III: SaaS + AI Hybrid Models: Economics and Investor Lens
In today’s market, most SaaS companies are no longer purely software providers. They are becoming intelligence platforms, integrating artificial intelligence into their products to enhance customer value. These hybrid models combine the predictability of SaaS with the innovation of AI. They hold great promises, but they also introduce new complexities in economics, margin structure, and investor expectations. For CFOs and CEOs, the challenge is not just understanding how these elements coexist but managing them in harmony to deliver profitable growth.
The hybrid SaaS-AI model is not simply the sum of its parts. It requires balancing two different economic engines: one that thrives on recurring, high-margin revenue and another that incurs variable costs linked to compute usage. The key to success lies in recognizing where AI enhances value and where it risks eroding profitability. Leaders who can measure, isolate, and manage these dynamics can unlock superior economics and investor confidence.
The Nature of Hybrid SaaS-AI Businesses
A hybrid SaaS-AI company starts with a core subscription-based platform. Customers pay recurring fees for access, support, and updates. Additionally, the company leverages AI-powered capabilities to enhance automation, personalization, analytics, and decision-making. These features can be embedded into existing workflows or offered as add-ons, sometimes billed based on usage.
Examples include CRMs with AI-assisted forecasting, HR platforms with intelligent candidate screening, or project tools with predictive insights. In each case, AI transforms user experience and perceived value, but it also introduces incremental cost per transaction. Every inference call, data model query, or real-time prediction consumes compute power and storage.
This hybridization reshapes the traditional SaaS equation. Revenue predictability remains strong due to base subscriptions, but gross margins become more variable. CFOs must now consider blended margins and segment economics. The task is to ensure that AI features expand total lifetime value faster than they inflate cost-to-serve.
Dual Revenue Streams and Pricing Design
Hybrid SaaS-AI companies often operate with two complementary revenue streams:
- Subscription Revenue: Fixed or tiered recurring revenue, predictable and contract-based.
- Usage-Based Revenue: Variable income tied to AI consumption, such as per query, token, or transaction.
This dual model offers flexibility. Subscriptions provide stability, while usage-based revenue captures upside from heavy engagement. However, it also complicates forecasting. CFOs must model revenue variance under various usage scenarios and clearly communicate these assumptions to the Board and investors.
Pricing design becomes a strategic lever. Some firms include AI features in premium tiers to encourage upgrades. Others use consumption pricing, passing compute costs directly to customers. The right approach depends on customer expectations, cost structure, and product positioning. For enterprise markets, predictable pricing is often a preferred option. For developer- or API-driven products, usage-based pricing aligns better with the delivery of value.
The most effective hybrid models structure pricing so that incremental revenue per usage exceeds incremental cost per usage. This ensures positive unit economics across both streams. Finance teams should run sensitivity analyses to test break-even points and adjust thresholds as compute expenses fluctuate.
Gross Margin Bifurcation
Gross margin in hybrid SaaS-AI companies must be analyzed in two layers:
- SaaS Core Margin: Typically, 75 to 85 percent is driven by software delivery, hosting, and support.
- AI Layer Margin: Often 40 to 60 percent, and it depends on compute efficiency and pricing.
When blended, the total margin may initially decline, especially if AI usage grows faster than subscription base revenue. The risk is that rising compute costs erode profitability before pricing can catch up. To manage this, CFOs should report segmented gross margins to the Board. This transparency helps avoid confusion when consolidated margins fluctuate.
The goal is not to immediately maximize blended margins, but to demonstrate a credible path toward margin expansion through optimization. Over time, as AI models become more efficient and the cost per inference declines, blended margins can recover. Finance teams should measure and communicate progress in terms of margin improvement per usage unit, not just overall percentages.
Impact on Customer Economics
AI features can materially improve customer economics. They increase stickiness, reduce churn, and create opportunities for upsell. A customer who utilizes AI-driven insights or automation tools is more likely to renew, as the platform becomes an integral part of their workflow. This improved retention directly translates into a higher lifetime value.
In some cases, AI features can also justify higher pricing or premium tiers. The key is measurable value. Customers pay more when they see clear ROI: for example, faster decision-making, labor savings, or improved accuracy. CFOs should work with product and customer success teams to quantify these outcomes and use them in renewal and pricing discussions.
The critical financial question is whether AI-enhanced LTV grows faster than CAC and variable cost. If so, AI drives profitable growth. If not, it becomes an expensive feature rather than a revenue engine. Regular cohort analysis helps ensure that AI adoption is correlated with improved unit economics.
Operating Leverage and Efficiency
Hybrid SaaS-AI companies must rethink operating leverage. Traditional SaaS gains leverage by spreading fixed costs over recurring revenue. In contrast, AI introduces variable costs tied to usage. This weakens the traditional leverage model. To restore it, finance leaders must focus on efficiency levers within AI operations.
Techniques such as caching, batching, and model optimization can reduce compute costs per request. Partnering with cloud providers for reserved capacity or leveraging model compression can further improve cost efficiency. The finance team’s role is to quantify these savings and ensure engineering priorities align with economic goals.
Another form of leverage comes from data reuse. The more a single model or dataset serves multiple customers or use cases, the higher the effective ROI on data and training investment. CFOs should track data utilization ratios and model reuse metrics as part of their financial dashboards.
Cash Flow and Capital Planning
Cash flow in hybrid businesses depends on the balance between stable subscription inflows and variable infrastructure outflows. CFOs must forecast not only revenue but also compute consumption. During early rollout, AI usage can spike unpredictably, leading to cost surges. Scenario planning is essential. Building buffers into budgets prevents margin shocks.
Capital allocation should prioritize scalability. Investments in AI infrastructure should follow demonstrated demand, not speculative projections. Over-provisioning GPU capacity can result in unnecessary cash expenditures. Many firms start with cloud credits or pay-as-you-go models before committing to long-term leases or hardware purchases. The objective is to match the cost ramp with revenue realization.
As with SaaS, negative working capital from annual prepayments can be used to fund expansion. However, CFOs should reserve portions of this cash for compute variability and cost optimization initiatives.
Investor Perspective
Investors view hybrid SaaS-AI models with both enthusiasm and scrutiny. They appreciate the potential for differentiation and pricing power, but expect clear evidence that AI integration enhances, rather than dilutes, economics. The investment thesis often centers on three questions:
- Does AI materially increase customer lifetime value?
- Can the company sustain or improve gross margins as AI usage scales?
- Is there a clear path to efficient growth under the Rule of 40?
Companies that answer yes to all three earn premium valuations. Investors will typically apply core SaaS multiples (5 to 8 times Annual Recurring Revenue, or ARR) with modest uplifts if AI features drive measurable revenue growth. However, if AI costs are poorly controlled or margins decline, valuations compress quickly.
To maintain investor confidence, CFOs must provide transparency. This includes segmented reporting, sensitivity scenarios, and clear explanations of cost drivers. Investors want to see not just innovation, but financial stewardship.
Strategic Positioning
The strategic role of AI within a SaaS company determines how investors perceive it. There are three broad positioning models:
- AI as a Feature: Enhances existing workflows but is not core to monetization. Example: an email scheduling tool with AI suggestions.
- AI as a Co-Pilot: Drives user productivity and becomes central to customer experience. Example: CRM with AI-generated insights.
- AI as a Platform: Powers entire ecosystems and opens new revenue lines. Example: a developer platform offering custom AI models.
Each model carries different costs and pricing implications. CFOs should ensure that the company’s financial model aligns with its strategic posture. A feature-based AI approach should be margin-accretive. A platform-based approach may accept lower margins initially in exchange for future ecosystem revenue.
Risk Management and Governance
Hybrid models also introduce new risks. Data privacy, model bias, and regulatory compliance can create unexpected liabilities. CFOs must ensure robust governance frameworks are in place. Insurance, audit, and legal teams should work closely together to manage exposure effectively. Transparency in AI decision-making builds customer trust and reduces reputational risk.
Another risk is dependency on third-party models or APIs. Companies that use external large language models face risks related to cost and reliability. CFOs should evaluate the total cost of ownership between building and buying AI capabilities. Diversifying across providers or developing proprietary models can mitigate concentration risk.
The CFO’s Role
In hybrid SaaS-AI organizations, the CFO’s role expands beyond financial reporting. Finance becomes the integrator of technology, strategy, and economics. The CFO must help design pricing strategies, measure the cost-to-serve, and effectively communicate value to investors. This requires fluency in both financial and technical language.
Regular dashboards should include metrics such as blended gross margin, compute cost per user, AI utilization rate, and LTV uplift resulting from AI adoption. This data-driven approach allows management to make informed trade-offs between innovation and profitability.
The CFO also acts as an educator. Boards and investors may not yet be familiar with AI-driven cost structures. Clear, simple explanations build confidence and support strategic decisions.
The Path Forward
The future belongs to companies that combine SaaS predictability with AI intelligence. Those who succeed will treat AI not as a novelty but as an economic engine. They will manage AI costs with the same rigor they apply to headcount or cloud spend. They will design pricing that reflects value creation, not just usage volume. And they will communicate to investors how each new AI feature strengthens the overall financial model.
Hybrid SaaS-AI companies occupy the forefront of modern business economics. They demonstrate that innovation and discipline are not opposites, but they are partners working toward a common objective. For CFOs and CEOs, the path forward is clear: measure what matters, value price, and guide the organization with transparency and foresight. Over time, this combination of creativity and control will separate enduring leaders from experimental wanderers.
Summary
In every business model, clarity around unit economics forms the foundation for sound decision-making. Whether one is building a SaaS company, an AI company, or a hybrid of both, understanding how revenue and costs behave at the most granular level allows management to design operations and financial models that scale intelligently. Without that clarity, growth becomes noise and is not sustainable.
From years of working across SaaS businesses, I have seen firsthand how the model rewards discipline. Predictable recurring revenue, high gross margins, and scalable operating leverage create a compounding effect when managed carefully. The challenge lies in balancing acquisition cost, retention, and cash efficiency, so that each new unit of growth strengthens rather than strains the business.
In AI, the economic story changes. Here, each unit of output incurs tangible costs, such as computation, data, and inference. The path to profitability lies not in volume alone, but in mastering the cost curve. Efficiency, model reuse, and pricing alignment become as critical as sales growth. AI firms must show investors that scaling demand will compress, not inflate, the cost per unit. I have no clue how they intend to do that with GPU demand going through the roof, but in this article, let us assume for giggles that there will be a light at the end of the tunnel, and GPU costs will temper down so it can fuel AI-driven business.
For hybrid SaaS-AI businesses, success depends on integration. AI should deepen customer value, expand lifetime revenue, and justify incremental costs. CFOs and CEOs must manage dual revenue streams, measure blended margins, and communicate transparently with investors about both the promise and the trade-offs of AI adoption.
Ultimately, understanding economics is knowing the truth. I am an economist, and I like to think I am unbiased. It enables leaders to align ambition with reality and design financial models that convey a credible narrative. As the lines between SaaS and AI continue to blur, those who understand the economics underlying innovation will be best equipped to build companies that endure.
Posted in Analytics, Business Process, Complexity, finance, Financial Metrics
Comments Off on Beyond the Buzz: The Real Economics Behind SaaS, AI, and Everything in Between
Tags: ai, business, finance, financial analysis, financial barometer, marketing, technology
Building a Lean Financial Infrastructure!
Posted by Hindol Datta
A lean financial infrastructure presumes the ability of every element in the value chain to preserve and generate cash flow. That is the fundamental essence of the lean infrastructure that I espouse. So what are the key elements that constitute a lean financial infrastructure?
And given the elements, what are the key tweaks that one must continually make to ensure that the infrastructure does not fall into entropy and the gains that are made fall flat or decay over time. Identification of the blocks and monitoring and making rapid changes go hand in hand.
The Key Elements or the building blocks of a lean finance organization are as follows:
- Chart of Accounts: This is the critical unit that defines the starting point of the organization. It relays and groups all of the key economic activities of the organization into a larger body of elements like revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities and equity. Granularity of these activities might lead to a fairly extensive chart of account and require more work to manage and monitor these accounts, thus requiring incrementally a larger investment in terms of time and effort. However, the benefits of granularity far exceeds the costs because it forces management to look at every element of the business.
- The Operational Budget: Every year, organizations formulate the operational budget. That is generally a bottoms up rollup at a granular level that would map to the Chart of Accounts. It might follow a top-down directive around what the organization wants to land with respect to income, expense, balance sheet ratios, et al. Hence, there is almost always a process of iteration in this step to finally arrive and lock down the Budget. Be mindful though that there are feeders into the budget that might relate to customers, sales, operational metrics targets, etc. which are part of building a robust operational budget.

- The Deep Dive into Variances: As you progress through the year and part of the monthly closing process, one would inquire about how the actual performance is tracking against the budget. Since the budget has been done at a granular level and mapped exactly to the Chart of Accounts, it thus becomes easier to understand and delve into the variances. Be mindful that every element of the Chart of Account must be evaluated. The general inclination is to focus on the large items or large variances, while skipping the small expenses and smaller variances. That method, while efficient, might not be effective in the long run to build a lean finance organization. The rule, in my opinion, is that every account has to be looked and the question should be – Why? If the management has agreed on a number in the budget, then why are the actuals trending differently. Could it have been the budget and that we missed something critical in that process? Or has there been a change in the underlying economics of the business or a change in activities that might be leading to these “unexpected variances”. One has to take a scalpel to both – favorable and unfavorable variances since one can learn a lot about the underlying drivers. It might lead to managerially doing more of the better and less of the worse. Furthermore, this is also a great way to monitor leaks in the organization. Leaks are instances of cash that are dropping out of the system. Much of little leaks amounts to a lot of cash in total, in some instances. So do not disregard the leaks. Not only will that preserve the cash but once you understand the leaks better, the organization will step up in efficiency and effectiveness with respect to cash preservation and delivery of value.

- Tweak the process: You will find that as you deep dive into the variances, you might want to tweak certain processes so these variances are minimized. This would generally be true for adverse variances against the budget. Seek to understand why the variance, and then understand all of the processes that occur in the background to generate activity in the account. Once you fully understand the process, then it is a matter of tweaking this to marginally or structurally change some key areas that might favorable resonate across the financials in the future.
- The Technology Play: Finally, evaluate the possibilities of exploring technology to surface issues early, automate repetitive processes, trigger alerts early on to mitigate any issues later, and provide on-demand analytics. Use technology to relieve time and assist and enable more thinking around how to improve the internal handoffs to further economic value in the organization.
All of the above relate to managing the finance and accounting organization well within its own domain. However, there is a bigger step that comes into play once one has established the blocks and that relates to corporate strategy and linking it to the continual evolution of the financial infrastructure.
The essential question that the lean finance organization has to answer is – What can the organization do so that we address every element that preserves and enhances value to the customer, and how do we eliminate all non-value added activities? This is largely a process question but it forces one to understand the key processes and identify what percentage of each process is value added to the customer vs. non-value added. This can be represented by time or cost dimension. The goal is to yield as much value added activities as possible since the underlying presumption of such activity will lead to preservation of cash and also increase cash acquisition activities from the customer.
Posted in Business Process, finance, Financial Process, Leadership, Learning Organization, Learning Process, Model Thinking, Risk Management
Tags: cash, finance, financial analysis, focus, lean organization, learning organization, organization architecture, organizational behavior, process, risk management, strategy, value chain