Category Archives: growth
Navigating Startup Growth: Adapting Your Operating Model Every Year
If a startup’s journey can be likened to an expedition up Everest, then its operating model is the climbing gear—vital, adaptable, and often revised. In the early stages, founders rely on grit and flexibility. But as companies ascend and attempt to scale, they face a stark and simple truth: yesterday’s systems are rarely fit for tomorrow’s challenges. The premise of this memo is equally stark: your operating model must evolve—consciously and structurally—every 12 months if your company is to scale, thrive, and remain relevant.
This is not a speculative opinion. It is a necessity borne out by economic theory, pattern recognition, operational reality, and the statistical arc of business mortality. According to a 2023 McKinsey report, only 1 in 200 startups make it to $100M in revenue, and even fewer become sustainably profitable. The cliff isn’t due to product failure alone—it’s largely an operational failure to adapt at the right moment. Let’s explore why.
1. The Law of Exponential Complexity
Startups begin with a high signal-to-noise ratio. A few people, one product, and a common purpose. Communication is fluid, decision-making is swift, and adjustments are frequent. But as the team grows from 10 to 50 to 200, each node adds complexity. If you consider the formula for potential communication paths in a group—n(n-1)/2—you’ll find that at 10 employees, there are 45 unique interactions. At 50? That number explodes to 1,225.
This isn’t just theory. Each of those paths represents a potential decision delay, misalignment, or redundancy. Without an intentional redesign of how information flows, how priorities are set, and how accountability is structured, the weight of complexity crushes velocity. An operating model that worked flawlessly in Year 1 becomes a liability in Year 3.
Lesson: The operating model must evolve to actively simplify while the organization expands.
2. The 4 Seasons of Growth
Companies grow in phases, each requiring different operating assumptions. Think of them as seasons:
| Stage | Key Focus | Operating Model Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Start-up | Product-Market Fit | Agile, informal, founder-centric |
| Early Growth | Customer Traction | Lean teams, tight loops, scalable GTM |
| Scale-up | Repeatability | Functional specialization, metrics |
| Expansion | Market Leadership | Cross-functional governance, systems |
At each transition, the company must answer: What must we centralize vs. decentralize? What metrics now matter? Who owns what? A model that optimizes for speed in Year 1 may require guardrails in Year 2. And in Year 3, you may need hierarchy—yes, that dreaded word among startups—to maintain coherence.
Attempting to scale without rethinking the model is akin to flying a Cessna into a hurricane. Many try. Most crash.
3. From Hustle to System: Institutionalizing What Works
Founders often resist operating models because they evoke bureaucracy. But bureaucracy isn’t the issue—entropy is. As the organization grows, systems prevent chaos. A well-crafted operating model does three things:
- Defines governance – who decides what, when, and how.
- Aligns incentives – linking strategy, execution, and rewards.
- Enables measurement – providing real-time feedback on what matters.
Let’s take a practical example. In the early days, a product manager might report directly to the CEO and also collaborate closely with sales. But once you have multiple product lines and a sales org with regional P&Ls, that old model breaks. Now you need Product Ops. You need roadmap arbitration based on capacity planning, not charisma.
Translation: Institutionalize what worked ad hoc by architecting it into systems.
4. Why Every 12 Months? The Velocity Argument
Why not every 24 months? Or every 6? The 12-month cadence is grounded in several interlocking reasons:
- Business cycles: Most companies operate on annual planning rhythms. You set targets, budget resources, and align compensation yearly. The operating model must match that cadence or risk misalignment.
- Cultural absorption: People need time to digest one operating shift before another is introduced. Twelve months is the Goldilocks zone—enough to evaluate results but not too long to become obsolete.
- Market feedback: Every year brings fresh feedback from the market, investors, customers, and competitors. If your operating model doesn’t evolve in step, you’ll lose your edge—like a boxer refusing to switch stances mid-fight.
And then there’s compounding. Like interest on capital, small changes in systems—when made annually—compound dramatically. Optimize decision velocity by 10% annually, and in 5 years, you’ve doubled it. Delay, and you’re crushed by organizational debt.
5. The Operating Model Canvas
To guide this evolution, we recommend using a simplified Operating Model Canvas—a strategic tool that captures the six dimensions that must evolve together:
| Dimension | Key Questions |
|---|---|
| Structure | How are teams organized? What’s centralized? |
| Governance | Who decides what? What’s the escalation path? |
| Process | What are the key workflows? How do they scale? |
| People | Do roles align to strategy? How do we manage talent? |
| Technology | What systems support this stage? Where are the gaps? |
| Metrics | Are we measuring what matters now vs. before? |
Reviewing and recalibrating these dimensions annually ensures that the foundation evolves with the building. The alternative is often misalignment, where strategy runs ahead of execution—or worse, vice versa.
6. Case Studies in Motion: Lessons from the Trenches
a. Slack (Pre-acquisition)
In Year 1, Slack’s operating model emphasized velocity of product feedback. Engineers spoke to users directly, releases shipped weekly, and product decisions were founder-led. But by Year 3, with enterprise adoption rising, the model shifted: compliance, enterprise account teams, and customer success became core to the GTM motion. Without adjusting the operating model to support longer sales cycles and regulated customer needs, Slack could not have grown to a $1B+ revenue engine.
b. Airbnb
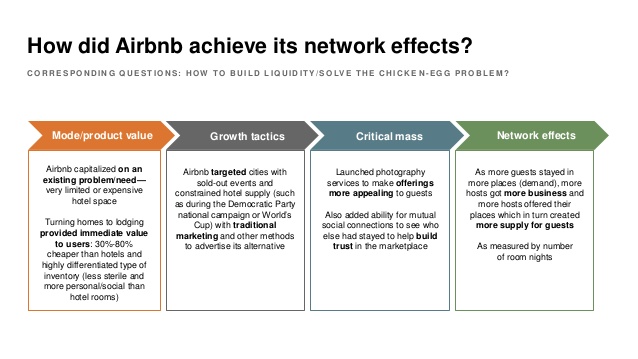
Initially, Airbnb’s operating rhythm centered on peer-to-peer UX. But as global regulatory scrutiny mounted, they created entirely new policy, legal, and trust & safety functions—none of which were needed in Year 1. Each year, Airbnb re-evaluated what capabilities were now “core” vs. “context.” That discipline allowed them to survive major downturns (like COVID) and rebound.
c. Stripe
Stripe invested heavily in internal tooling as they scaled. Recognizing that developer experience was not only for customers but also internal teams, they revised their internal operating platforms annually—often before they were broken. The result: a company that scaled to serve millions of businesses without succumbing to the chaos that often plagues hypergrowth.
7. The Cost of Inertia
Aging operating models extract a hidden tax. They confuse new hires, slow decisions, demoralize high performers, and inflate costs. Worse, they signal stagnation. In a landscape where capital efficiency is paramount (as underscored in post-2022 venture dynamics), bloated operating models are a death knell.
Consider this: According to Bessemer Venture Partners, top quartile SaaS companies show Rule of 40 compliance with fewer than 300 employees per $100M of ARR. Those that don’t? Often have twice the headcount with half the profitability—trapped in models that no longer fit their stage.
8. How to Operationalize the 12-Month Reset
For practical implementation, I suggest a 12-month Operating Model Review Cycle:
| Month | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Jan | Strategic planning finalization |
| Feb | Gap analysis of current model |
| Mar | Cross-functional feedback loop |
| Apr | Draft new operating model vNext |
| May | Review with Exec Team |
| Jun | Pilot model changes |
| Jul | Refine and communicate broadly |
| Aug | Train managers on new structures |
| Sep | Integrate into budget planning |
| Oct | Lock model into FY plan |
| Nov | Run simulations/test governance |
| Dec | Prepare for January launch |
This cycle ensures that your org model does not lag behind your strategic ambition. It also sends a powerful cultural signal: we evolve intentionally, not reactively.
Conclusion: Be the Architect, Not the Archaeologist
Every successful company is, at some level, a systems company. Apple is as much about its supply chain as its design. Amazon is a masterclass in operating cadence. And Salesforce didn’t win by having a better CRM—it won by continuously evolving its go-to-market and operating structure.
To scale, you must be the architect of your company’s operating future—not an archaeologist digging up decisions made when the world was simpler.
So I leave you with this conviction: operating models are not carved in stone—they are coded in cycles. And the companies that win are those that rewrite that code every 12 months—with courage, with clarity, and with conviction.
Precision at Scale: How to Grow Without Drowning in Complexity
In business, as in life, scale is seductive. It promises more of the good things—revenue, reach, relevance. But it also invites something less welcome: complexity. And the thing about complexity is that it doesn’t ask for permission before showing up. It simply arrives, unannounced, and tends to stay longer than you’d like.
As we pursue scale, whether by growing teams, expanding into new markets, or launching adjacent product lines, we must ask a question that seems deceptively simple: how do we know we’re scaling the right way? That question is not just philosophical—it’s deeply economic. The right kind of scale brings leverage. The wrong kind brings entropy.

Now, if I’ve learned anything from years of allocating capital, it is this: returns come not just from growth, but from managing the cost and coordination required to sustain that growth. In fact, the most successful enterprises I’ve seen are not the ones that scaled fastest. They’re the ones that scaled precisely. So, let’s get into how one can scale thoughtfully, without overinvesting in capacity, and how to tell when the system you’ve built is either flourishing or faltering.
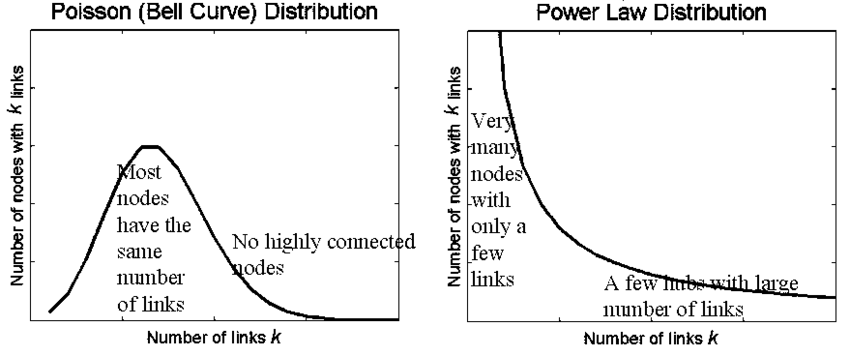
To begin, one must understand that scale and complexity do not rise in parallel; complexity has a nasty habit of accelerating. A company with two teams might have a handful of communication lines. Add a third team, and you don’t just add more conversations—you add relationships between every new and existing piece. In engineering terms, it’s a combinatorial explosion. In business terms, it’s meetings, misalignment, and missed expectations.
Cities provide a useful analogy. When they grow in population, certain efficiencies appear. Infrastructure per person often decreases, creating cost advantages. But cities also face nonlinear rises in crime, traffic, and disease—all manifestations of unmanaged complexity. The same is true in organizations. The system pays a tax for every additional node, whether that’s a service, a process, or a person. That tax is complexity, and it compounds.
Knowing this, we must invest in capacity like we would invest in capital markets—with restraint and foresight. Most failures in capacity planning stem from either a lack of preparation or an excess of confidence. The goal is to invest not when systems are already breaking, but just before the cracks form. And crucially, to invest no more than necessary to avoid those cracks.
Now, how do we avoid overshooting? I’ve found that the best approach is to treat capacity like runway. You want enough of it to support takeoff, but not so much that you’ve spent your fuel on unused pavement. We achieve this by investing in increments, triggered by observable thresholds. These thresholds should be quantitative and predictive—not merely anecdotal. If your servers are running at 85 percent utilization across sustained peak windows, that might justify additional infrastructure. If your engineering lead time starts rising despite team growth, it suggests friction has entered the system. Either way, what you’re watching for is not growth alone, but whether the system continues to behave elegantly under that growth.
Elegance matters. Systems that age well are modular, not monolithic. In software, this might mean microservices that scale independently. In operations, it might mean regional pods that carry their own load, instead of relying on a centralized command. Modular systems permit what I call “selective scaling”—adding capacity where needed, without inflating everything else. It’s like building a house where you can add another bedroom without having to reinforce the foundation. That kind of flexibility is worth gold.
Of course, any good decision needs a reliable forecast behind it. But forecasting is not about nailing the future to a decimal point. It is about bounding uncertainty. When evaluating whether to scale, I prefer forecasts that offer a range—base, best, and worst-case scenarios—and then tie investment decisions to the 75th percentile of demand. This ensures you’re covering plausible upside without betting on the moon.
Let’s not forget, however, that systems are only as good as the signals they emit. I’m wary of organizations that rely solely on lagging indicators like revenue or margin. These are important, but they are often the last to move. Leading indicators—cycle time, error rates, customer friction, engineer throughput—tell you much sooner whether your system is straining. In fact, I would argue that latency, broadly defined, is one of the clearest signs of stress. Latency in delivery. Latency in decisions. Latency in feedback. These are the early whispers before systems start to crack.
To measure whether we’re making good decisions, we need to ask not just if outcomes are improving, but if the effort to achieve them is becoming more predictable. Systems with high variability are harder to scale because they demand constant oversight. That’s a recipe for executive burnout and organizational drift. On the other hand, systems that produce consistent results with declining variance signal that the business is not just growing—it’s maturing.
Still, even the best forecasts and the finest metrics won’t help if you lack the discipline to say no. I’ve often told my teams that the most underrated skill in growth is the ability to stop. Stopping doesn’t mean failure; it means the wisdom to avoid doubling down when the signals aren’t there. This is where board oversight matters. Just as we wouldn’t pour more capital into an underperforming asset without a turn-around plan, we shouldn’t scale systems that aren’t showing clear returns.
So when do we stop? There are a few flags I look for. The first is what I call capacity waste—resources allocated but underused, like a datacenter running at 20 percent utilization, or a support team waiting for tickets that never come. That’s not readiness. That’s idle cost. The second flag is declining quality. If error rates, customer complaints, or rework spike following a scale-up, then your complexity is outpacing your coordination. Third, I pay attention to cognitive load. When decision-making becomes a game of email chains and meeting marathons, it’s time to question whether you’ve created a machine that’s too complicated to steer.
There’s also the budget creep test. If your capacity spending increases by more than 10 percent quarter over quarter without corresponding growth in throughput, you’re not scaling—you’re inflating. And in inflation, as in business, value gets diluted.
One way to guard against this is by treating architectural reserves like financial ones. You wouldn’t deploy your full cash reserve just because an opportunity looks interesting. You’d wait for evidence. Similarly, system buffers should be sized relative to forecast volatility, not organizational ambition. A modest buffer is prudent. An oversized one is expensive insurance.
Some companies fall into the trap of building for the market they hope to serve, not the one they actually have. They build as if the future were guaranteed. But the future rarely offers such certainty. A better strategy is to let the market pull capacity from you. When customers stretch your systems, then you invest. Not because it’s a bet, but because it’s a reaction to real demand.
There’s a final point worth making here. Scaling decisions are not one-time events. They are sequences of bets, each informed by updated evidence. You must remain agile enough to revise the plan. Quarterly evaluations, architectural reviews, and scenario testing are the boardroom equivalent of course correction. Just as pilots adjust mid-flight, companies must recalibrate as assumptions evolve.
To bring this down to earth, let me share a brief story. A fintech platform I advised once found itself growing at 80 percent quarter over quarter. Flush with success, they expanded their server infrastructure by 200 percent in a single quarter. For a while, it worked. But then something odd happened. Performance didn’t improve. Latency rose. Error rates jumped. Why? Because they hadn’t scaled the right parts. The orchestration layer, not the compute layer, was the bottleneck. Their added capacity actually increased system complexity without solving the real issue. It took a re-architecture, and six months of disciplined rework, to get things back on track. The lesson: scaling the wrong node is worse than not scaling at all.
In conclusion, scale is not the enemy. But ungoverned scale is. The real challenge is not growth, but precision. Knowing when to add, where to reinforce, and—perhaps most crucially—when to stop. If we build systems with care, monitor them with discipline, and remain intellectually honest about what’s working, we give ourselves the best chance to grow not just bigger, but better.
And that, to borrow a phrase from capital markets, is how you compound wisely.
Managing Scale
| I think the most difficult thing had been scaling the infrastructure. Trying to support the response we had received from our users and the number of people that were interested in using the software. – Shawn Fanning |
Froude’s number? It is defined as the square of the ship’s velocity divided by its length and multiplied by the acceleration caused by gravity. So why are we introducing ships in this chapter? As I have done before, I am liberally standing on the shoulder of the giant, Geoffrey West, and borrowing from his account on the importance of the Froude’s number and the practical implications. Since ships are subject to turbulence, using a small model that works in a simulated turbulent environment might not work when we manufacture a large ship that is facing the ebbs and troughs of a finicky ocean. The workings and impact of turbulence is very complex, and at scale it becomes even more complex. Froude’s key contribution was to figure out a mathematical pathway of how to efficiently and effectively scale from a small model to a practical object. He did that by using a ratio as the common denominator. Mr. West provides an example that hits home: How fast does a 10-foot-long ship have to move to mimic the motion of a 700-foot-long ship moving at 20 knots. If they are to have the same Froude number (that is, the same value of the square of their velocity divided by their length), then the velocity has to scale as the square root of their lengths. The ratio of the square root of their lengths is the the square of 700 feet of the ship/10 feet of the model ship which turns out to be the square of 70. For the 10-foot model to mimic the motion of a large ship, it must move at the speed of 20 knots/ square of 70 or 2.5 knots. The Froude number is still widely used across many fields today to bridge small scale and large-scale thinking. Although this number applies to physical systems, the notion that adaptive systems can be similarly bridged through appropriate mathematical equations. Unfortunately, because of the increased number of variables impacting adaptive systems and all of these variables working and learning from one another, the task of establishing a Froude number becomes diminishingly small.

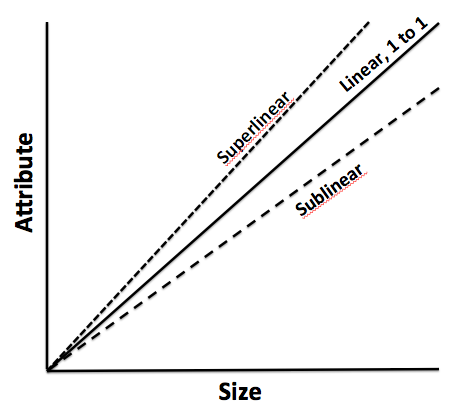
The other concept that has gained wide attention is the science of allometry. Allometry essentially states that as size increases, then the form of the object would change. Allometric scaling governs all complex physical and adaptive systems. So the question is whether there are some universal laws or mathematics that can be used to enable us to better understand or predict scale impacts. Let us extend this thinking a bit further. If sizes influence form and form constitute all sub-physical elements, then it would stand to reason that a universal law or a set of equations can provide deep explanatory powers on scale and systems. One needs to bear in mind that even what one might consider a universal law might be true within finite observations and boundaries. In other words, if there are observations that fall outside of those boundaries, one is forced into resetting our belief in the universal law or to frame a new paradigm to cover these exigencies. I mention this because as we seek to understand business and global grand challenges considering the existence of complexity, scale, chaos and seeming disorder – we might also want to embrace multiple laws or formulations working at different hierarchies and different data sets to arrive at satisficing solutions to the problems that we want to wrestle with.
Physics and mathematics allow a qualitatively high degree of predictability. One can craft models across different scales to make a sensible approach on how to design for scale. If you were to design a prototype using a 3D printer and decide to scale that prototype a 100X, there are mathematical scalar components that are factored into the mechanics to allow for some sort of equivalence which would ultimately lead to the final product fulfilling its functional purpose in a complex physical system. But how does one manage scale in light of those complex adaptive systems that emerge due to human interactions, evolution of organization, uncertainty of the future, and dynamic rules that could rapidly impact the direction of a company?
Is scale a single measure? Or is it a continuum? In our activities, we intentionally or unintentionally invoke scale concepts. What is the most efficient scale to measure an outcome, so we can make good policy decisions, how do we apply our learning from one scale to a system that operates on another scale and how do we assess how sets of phenomena operate at different scales, spatially and temporally, and how they impact one another? Now the most interesting question: Is scale polymorphous? Does the word scale have different meanings in different contexts? When we talk about microbiology, we are operating at micro-scales. When we talk at a very macro level, our scales are huge. In business, we regard scale with respect to how efficiently we grow. In one way, it is a measure but for the following discussion, we will interpret scale as non-linear growth expending fewer and fewer resources to support that growth as a ratio.

As we had discussed previously, complex adaptive systems self-organize over time. They arrive at some steady state outcome without active intervention. In fact, the active intervention might lead to unintended consequences that might even spell doom for the system that is being influenced. So as an organization scales, it is important to keep this notion of rapid self-organization in mind which will inform us to make or not make certain decisions from a central or top-down perspective. In other words, part of managing scale successfully is to not manage it at a coarse-grained level.
The second element of successfully managing scale is to understand the constraints that prevent scale. There is an entire chapter dedicated to the theory of constraints which sheds light on why this is a fundamental process management technique that increases the pace of the system. But for our purposes in this section, we will summarize as follows: every system as it grows have constraints. It is important to understand the constraints because these constraints slow the system: the bottlenecks have to be removed. And once one constraint is removed, then one comes across another constraint. The system is a chain of events and it is imperative that all of these events are identified. The weakest links harangue the systems and these weakest links have to be either cleared or resourced to enable the system to scale. It is a continuous process of observation and tweaking the results with the established knowledge that the demons of uncertainty and variability can reset the entire process and one might have to start again. Despite that fact, constraint management is an effective method to negotiate and manage scale.

The third element is devising the appropriate organization architecture. As one projects into the future, management might be inclined toward developing and investing in the architecture early to accommodate the scale. Overinvestment in the architecture might not be efficient. As mentioned, cities and social systems that grow 100% require 85% investment in infrastructure: in other words, systems grow on a sublinear scale from an infrastructure perspective. How does management of scale arrive at the 85%? It is nigh impossible, but it is important to reserve that concept since it informs management to architect the infrastructure cautiously. Large investments upfront could be a waste or could slow the system down: alternative, investments that are postponed a little too late can also impact the system adversely.
The fourth element of managing scale is to focus your lens of opportunity. In macroecology, we can arrive at certain conclusions when we regard the system from a distance versus very closely. We can subsume our understanding into one big bucket called climate change and then we figure out different ways to manage the complexity that causes the climate change by invoking certain policies and incentives at a macro level. However, if we go closer, we might decide to target a very specific contributor to climate change – namely, fossil fuels. The theory follows that to manage the dynamic complexity and scale of climate impact – it would be best to address a major factor which, in this case, would be fossil fuels. The equivalence of this in a natural business setting would be to establish and focus the strategy for scale in a niche vertical or a relatively narrower set of opportunities. Even though we are working in the web of complex adaptive systems, we might devise strategies to directionally manage the business within the framework of complex physical systems where we have an understanding of the slight variations of initial state and the realization that the final outcome might be broad but yet bounded for intentional management.

The final element is the management of initial states. Complex physical systems are governed by variation in initial states. Perturbation of these initial states can lead to a wide divergence of outcomes, albeit bounded within a certain frame of reference. It is difficult perhaps to gauge all the interactions that might occur from a starting point to the outcome, although we agree that a few adjustments like decentralization of decision making, constraint management, optimal organization structure and narrowing the playing field would be helpful.
Internal versus External Scale
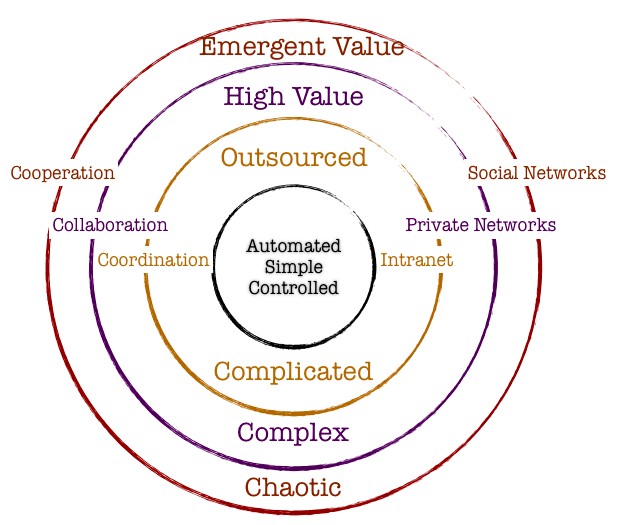
This article discusses internal and external complexity before we tee up a more detailed discussion on internal versus external scale. This chapter acknowledges that complex adaptive systems have inherent internal and external complexities which are not additive. The impact of these complexities is exponential. Hence, we have to sift through our understanding and perhaps even review the salient aspects of complexity science which have already been covered in relatively more detail in earlier chapter. However, revisiting complexity science is important, and we will often revisit this across other blog posts to really hit home the fundamental concepts and its practical implications as it relates to management and solving challenges at a business or even a grander social scale.

A complex system is a part of a larger environment. It is a safe to say that the larger environment is more complex than the system itself. But for the complex system to work, it needs to depend upon a certain level of predictability and regularity between the impact of initial state and the events associated with it or the interaction of the variables in the system itself. Note that I am covering both – complex physical systems and complex adaptive systems in this discussion. A system within an environment has an important attribute: it serves as a receptor to signals of external variables of the environment that impact the system. The system will either process that signal or discard the signal which is largely based on what the system is trying to achieve. We will dedicate an entire article on system engineering and thinking later, but the uber point is that a system exists to serve a definite purpose. All systems are dependent on resources and exhibits a certain capacity to process information. Hence, a system will try to extract as many regularities as possible to enable a predictable dynamic in an efficient manner to fulfill its higher-level purpose.
Let us understand external complexities. We can interchangeably use the word environmental complexity as well. External complexity represents physical, cultural, social, and technological elements that are intertwined. These environments beleaguered with its own grades of complexity acts as a mold to affect operating systems that are mere artifacts. If operating systems can fit well within the mold, then there is a measure of fitness or harmony that arises between an internal complexity and external complexity. This is the root of dynamic adaptation. When external environments are very complex, that means that there are a lot of variables at play and thus, an internal system has to process more information in order to survive. So how the internal system will react to external systems is important and they key bridge between those two systems is in learning. Does the system learn and improve outcomes on account of continuous learning and does it continually modify its existing form and functional objectives as it learns from external complexity? How is the feedback loop monitored and managed when one deals with internal and external complexities? The environment generates random problems and challenges and the internal system has to accept or discard these problems and then establish a process to distribute the problems among its agents to efficiently solve those problems that it hopes to solve for. There is always a mechanism at work which tries to align the internal complexity with external complexity since it is widely believed that the ability to efficiently align the systems is the key to maintaining a relatively competitive edge or intentionally making progress in solving a set of important challenges.
Internal complexity are sub-elements that interact and are constituents of a system that resides within the larger context of an external complex system or the environment. Internal complexity arises based on the number of variables in the system, the hierarchical complexity of the variables, the internal capabilities of information pass-through between the levels and the variables, and finally how it learns from the external environment. There are five dimensions of complexity: interdependence, diversity of system elements, unpredictability and ambiguity, the rate of dynamic mobility and adaptability, and the capability of the agents to process information and their individual channel capacities.

If we are discussing scale management, we need to ask a fundamental question. What is scale in the context of complex systems? Why do we manage for scale? How does management for scale advance us toward a meaningful outcome? How does scale compute in internal and external complex systems? What do we expect to see if we have managed for scale well? What does the future bode for us if we assume that we have optimized for scale and that is the key objective function that we have to pursue?