Category Archives: Financial Metrics
How Strategic CFOs Drive Sustainable Growth and Change
When people ask me what the most critical relationship in a company really is, I always say it’s the one between the CEO and the CFO. And no, I am not being flippant. In my thirty years helping companies manage growth, navigate crises, and execute strategic shifts, the moments that most often determine success or spiraled failure often rests on how tightly the CEO and CFO operate together. One sets a vision. The other turns aspiration into action. Alone, each has influence; together, they can transform the business.
Transformation, after all, is not a project. It is a culture shift, a strategic pivot, a redefinition of operating behaviors. It’s more art than engineering and more people than process. And at the heart of it lies a fundamental tension: You need ambition, yet you must manage risk. You need speed, but you cannot abandon discipline. You must pursue new business models while preserving your legacy foundations. In short, you need to build simultaneously on forward momentum and backward certainty.
That complexity is where the strategic CFO becomes indispensable. The CFO’s job is not just to count beans, it’s to clear the ground where new plants can grow. To unlock capital without unleashing chaos. To balance accountable rigor with growth ambition. To design transformation from the numbers up, not just hammer it into the planning cycle. When this role is fulfilled, the CEO finds their most trusted confidante, collaborator, and catalyst.
Think of it this way. A CEO paints a vision: We must double revenue, globalize our go-to-market, pivot into new verticals, revamp the product, or embrace digital. It sounds exciting. It feels bold. But without a financial foundation, it becomes delusional. Does the company have the cash runway? Can the old cost base support the new trajectory? Are incentives aligned? Are the systems ready? Will the board nod or push back? Who is accountable if sales forecast misses or an integration falters? A CFO’s strategic role is to bring those questions forward not cynically, but constructively—so the ambition becomes executable.
The best CEOs I’ve worked with know this partnership instinctively. They build strategy as much with the CFO as with the head of product or sales. They reward honest challenge, not blind consensus. They request dashboards that update daily, not glossy decks that live in PowerPoint. They ask, “What happens to operating income if adoption slows? Can we reverse full-time hiring if needed? Which assumptions unlock upside with minimal downside?” Then they listen. And change. That’s how transformation becomes durable.
Let me share a story. A leader I admire embarked on a bold plan: triple revenue in two years through international expansion and a new channel model. The exec team loved the ambition. Investors cheered. But the CFO, without hesitation, did not say no. She said let us break it down. Suppose it costs $30 million to build international operations, $12 million to fund channel enablement, plus incremental headcount, marketing expenses, R&D coordination, and overhead. Let us stress test the plan. What if licensing stalls? What if fulfillment issues delay launches? What if cross-border tax burdens permanently drag down the margin?
The CEO wanted the bold headline number. But together, they translated it into executable modules. They set up rolling gates: a $5 million pilot, learn, fund next $10 million, learn, and so on. They built exit clauses. They aligned incentives so teams could pivot without losing credibility. They also built redundancy into systems and analytics, with daily data and optionality-based budgeting. The CEO had the vision, but the CFO gave it a frame. That is partnership.
That framing role extends beyond capital structure or P&L. It bleeds into operating rhythm. The strategic CFO becomes the architect of transformation cadence. They design how weekly, monthly, and quarterly look and feel. They align incentive schemes so that geography may outperform globally while still holding central teams accountable. They align finance, people, product, and GTM teams to shared performance metrics—not top-level vanity metrics, but actionable ones: user engagement, cost per new customer, onboarding latency, support burden, renewal velocity. They ensure data is not stashed in silos. They make it usable, trusted, visible. Because transformation is only as effective as your ability to measure missteps, iterate, and learn.
This is why I say the CFO becomes a strategic weapon: a lever for insight, integration, and investment.
Boards understand this too, especially when it is too late. They see CEOs who talk of digital transformation while still approving global headcount hikes. They see operating legacy systems still dragging FY ‘Digital 2.0’ ambition. They see growth funded, but debt rising with little structural benefit. In those moments, they turn to the CFO. The board does not ask the CFO if they can deliver the numbers. They ask whether the CEO can. They ask, “What’s the downside exposure? What are the guardrails? Who is accountable? How long will transformation slow profitability? And can we reverse if needed?”
That board confidence, when positive, is not accidental. It comes from a CFO who built that trust, not by polishing a spreadsheet, but by building strategy together, testing assumptions early, and designing transformation as a financial system.
Indeed, transformation without control is just creative destruction. And while disruption may be trendy, few businesses survive without solid footing. The CFO ensures that disruption does not become destruction. That investments scale with impact. That flexibility is funded. That culture is not ignored. That when exceptions arise, they do not unravel behaviors, but refocus teams.
This is often unseen. Because finance is a support function, not a front-facing one. But consider this: it is finance that approves the first contract. Finance assists in setting the commission structure that defines behavior. Finance sets the credit policy, capital constraints, and invoice timing, and all of these have strategic logic. A CFO who treats each as a tactical lever becomes the heart of transformation.
Take forecasting. Transformation cannot run on backward-moving averages. Yet too many companies rely on year-over-year rates, lagged signals, and static targets. The strategic CFO resurrects forecasting. They bring forward leading indicators of product usage, sales pipeline, supply chain velocity. They reframe forecasts as living systems. We see a dip? We call a pivot meeting. We see high churn? We call the product team. We see hiring cost creep? We call HR. Forewarned is forearmed. That is transformation in flight.
On the capital front, the CFO becomes a barbell strategist. They pair patient growth funding with disciplined structure. They build in fields of optionality: reserves for opportunistic moves, caps on unfunded headcount, staged deployment, and scalable contracts. They calibrate pricing experiments. They design customer acquisition levers with off ramps. They ensure that at every step of change, you can set a gear to reverse—without losing momentum, but with discipline.
And they align people. Transformation hinges on mindset. In fast-moving companies, people often move faster than they think. Great leaders know this. The strategic CFO builds transparency into compensation. They design equity vesting tied to transformation metrics. They design long-term incentives around cross-functional execution. They also design local authority within discipline. Give leaders autonomy, but align them to the rhythm of finance. Even the best strategy dies when every decision is a global approval. Optionality must scale with coordination.
Risk management transforms too. In the past, the CFO’s role in transformation was to shield operations from political turbulence. Today, it is to internally amplify controlled disruption. That means modeling volatility with confidence. Scenario modeling under market shock, regulatory shift, customer segmentation drift. Not just building firewalls, but designing escape ramps and counterweights. A transformation CFO builds risk into transformation—but as a system constraint to be managed, not a gate to prevent ambition.
I once had a CEO tell me they felt alone when delivering digital transformation. HR was not aligned. Product was moving too slowly. Sales was pushing legacy business harder. The CFO had built a bridge. They brought HR, legal, sales, and marketing into weekly update sessions, each with agreed metrics. They brokered resolutions. They surfaced trade-offs confidently. They pressed accountability floor—not blame, but clarity. That is partnership. That is transformation armor.
Transformation also triggers cultural tectonics. And every tectonic shift features friction zones—power renegotiation, process realignment, work redesign. Without financial discipline, politics wins. Mistrust builds. Change derails. The strategic CFO intervenes not as a policeman, but as an arbiter of fairness: If people are asked to stretch, show them the ROI. If processes migrate, show them the rationale. If roles shift, unpack the logic. Maintaining trust alignment during transformation is as important as securing funding.
The ability to align culture, capital, cadence, and accountability around a single north star—that is the strategic CFO’s domain.
And there is another hidden benefit: the CFO’s posture sets the tone for transformation maturity. CFOs who co-create, co-own, and co-pivot build transformation muscle. Those companies that learn together scale transformation together.
I once wrote that investors will forgive a miss if the learning loops are obvious. That is also true inside the company. When a CEO and CFO are aligned, and the CFO is the first to acknowledge what is not working to expectations, when pivots are driven by data rather than ego, that establishes the foundation for resilient leadership. That is how companies rebuild trust in growth every quarter. That is how transformation becomes a norm.
If there is a fear inside the CFO community, it is the fear of being visible. A CFO may believe that financial success is best served quietly. But the moment they step confidently into transformation, they change that dynamic. They say: Yes, we own the books. But we also own the roadmap. Yes, we manage the tail risk. But we also amplify the tail opportunity. That mindset is contagious. It builds confidence across the company and among investors. That shift in posture is more valuable than any forecast.
So let me say it again. Strategy is not a plan. Mechanics do not make execution. Systems do. And at the junction of vision and execution, between boardroom and frontline, stands the CFO. When transformation is on the table, the CFO walks that table from end to end. They make sure the chairs are aligned. The evidence is available. The accountability is shared. The capital is allocated, measured, and adapted.
This is why I refer to the CFO as the CEO’s most important ally. Not simply a confidante. Not just a number-cruncher. A partner in purpose. A designer of execution. A steward of transformation. Which is why, if you are a CFO reading this, I encourage you: step forward. You do not need permission to rethink transformation. You need conviction to shape it. And if you can build clarity around capital, establish a cadence for metrics, align incentives, and implement systems for governance, you will make your CEO’s job easier. You will elevate your entire company. You will unlock optionality not just for tomorrow, but for the years that follow. Because in the end, true transformation is not a moment. It is a movement. And the CFO, when prepared, can lead it.
The Power of Customer Lifetime Value in Modern Business
In contemporary business discourse, few metrics carry the strategic weight of Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). CLV and CAC are prime metrics. For modern enterprises navigating an era defined by digital acceleration, subscription economies, and relentless competition, CLV represents a unifying force, uniting finance, marketing, and strategy into a single metric that measures not only transactions but also the value of relationships. Far more than a spreadsheet calculation, CLV crystallizes lifetime revenue, loyalty, referral impact, and long-term financial performance into a quantifiable asset.
This article explores CLV’s origins, its mathematical foundations, its role as a strategic North Star across organizational functions, and the practical systems required to integrate it fully into corporate culture and capital allocation. It also highlights potential pitfalls and ethical implications.
I. CLV as a Cross-Functional Metric
CLV evolved from a simple acknowledgement: not all customers are equally valuable, and many businesses would prosper more by nurturing relationships than chasing clicks. The transition from single-sale tallies to lifetime relationship value gained momentum with the rise of subscription models—telecom plans, SaaS platforms, and membership programs—where the fiscal significance of recurring revenue became unmistakable.
This shift reframed capital deployment and decision-making:
- Marketing no longer seeks volume unquestioningly but targets segments with high long-term value.
- Finance integrates CLV into valuation models and capital allocation frameworks.
- Strategy uses it to guide M&A decisions, pricing stratagems, and product roadmap prioritization.
Because CLV is simultaneously a financial measurement and a customer-centric tool, it builds bridges—translating marketing activation into board-level impact.
II. How to calculate CLV
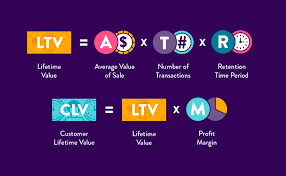
At its core, CLV employs economic modeling similar to net present value. A basic formula:
CLV = ∑ (t=0 to T) [(Rt – Ct) / (1 + d)^t]
- Rt = revenue generated at time t
- Ct = cost to serve/acquire at time t
- d = discount rate
- T = time horizon
This anchors CLV in well-accepted financial principles: discounted future cash flows, cost allocation, and multi-period forecasting. It satisfies CFO requirements for rigor and measurability.
However, marketing leaders often expand this to capture:
- Referral value (Rt includes not just direct sales, but influenced purchases)
- Emotional or brand-lift dimensions (e.g., window customers who convert later)
- Upselling, cross-selling, and tiered monetization over time
These expansions refine CLV into a dynamic forecast rather than a static average—one that responds to segmentation and behavioral triggers.
III. CLV as a Board-Level Metric
A. Investment and Capital Prioritization
Traditional capital decisions rely on ROI, return on invested capital (ROIC), and earnings multiples. CLV adds nuance: it gauges not only immediate returns but extended client relationships. This enables an expanded view of capital returns.
For example, a company might shift budget from low-CLV acquisition channels to retention-focused strategies—investing more in on-boarding, product experience, or customer success. These initiatives, once considered costs, now become yield-generating assets.
B. Segment-Based Acquisition
CLV enables precision targeting. A segment that delivers a 6:1 lifetime value-to-acquisition-cost (LTV:CAC) ratio is clearly more valuable than one delivering 2:1. Marketing reallocates spend accordingly, optimizing strategic segmentation and media mix, tuning messaging for high-value cohorts.
Because CLV is quantifiable and forward-looking, it naturally aligns marketing decisions with shareholder-driven metrics.
C. Tiered Pricing and Customer Monetization
CLV is also central to monetization strategy. Churn, upgrade rates, renewal behaviors, and pricing power all can be evaluated through the lens of customer value over time. Versioning, premium tiers, loyalty benefits—all become levers to maximize lifetime value. Finance and strategy teams model these scenarios to identify combinations that yield optimal returns.
D. Strategic Partnerships and M&A
CLV informs deeper decisions about partnerships and mergers. In evaluating a potential platform acquisition, projected contribution to overall CLV may be a decisive factor, especially when combined customer pools or cross-sell ecosystems can amplify lifetime revenue. It embeds customer value insights into due diligence and valuation calculations.
IV. Organizational Integration: A Strategic Imperative
Effective CLV deployment requires more than good analytics—it demands structural clarity and cultural alignment across three key functions.
A. Finance as Architect
Finance teams frame the assumptions—discount rates, cost allocation, margin calibration—and embed CLV into broader financial planning and analysis. Their task: convert behavioral data and modeling into company-wide decision frameworks used in investment reviews, budgeting, and forecasting processes.
B. Marketing as Activation Engine
Marketing owns customer acquisition, retention campaigns, referral programs, and product messaging. Their role is to feed the CLV model with real data: conversion rates, churn, promotion impact, and engagement flows. In doing so, campaigns become precision tools tuned to maximize customer yield rather than volume alone.
C. Strategy as Systems Designer
The strategy team weaves CLV outputs into product roadmaps, pricing strategy, partnership design, and geographic expansion. Using CLV foliated by cohort and channel, strategy leaders can sequence investments to align with long-term margin objectives—such as a five-year CLV-driven revenue mix.
V. Embedding CLV Into Corporate Processes
The following five practices have proven effective at embedding CLV into organizational DNA:
- Executive Dashboards
Incorporate LTV:CAC ratios, cohort retention rates, and segment CLV curves into executive reporting cycles. Tie leadership incentives (e.g., bonuses, compensation targets) to long-term value outcomes. - Cross-Functional CLV Cells
Establish CLV analytics teams staffed by finance, marketing insights, and data engineers. They own CLV modeling, simulation, and distribution across functions. - Monthly CLV Reviews
Monthly orchestration meetings integrate metrics updates, marketing feedback on campaigns, pricing evolution, and retention efforts. Simultaneous adjustment across functions allows dynamic resource allocation. - Capital Allocation Gateways
Projects involving customer-facing decisions—from new products to geographic pullbacks—must include CLV impact assessments in gating criteria. These can also feed into product investment requests and ROI thresholds. - Continuous Learning Loops
CLV models must be updated with actual lifecycle data. Regular recalibration fosters learning from retention behaviors, pricing experiments, churn drivers, and renewal rates—fueling confidence in incremental decision-making.
VI. Caveats and Limitations
CLV, though powerful, is not a cure-all. These caveats merit attention:
- Data Quality: Poorly integrated systems, missing customer identifiers, or inconsistent cohort logic can produce misleading CLV metrics.
- Assumption Risk: Discount rates, churn decay, turnaround behavior—all are model assumptions. Unqualified confidence can mislead investment.
- Narrow Focus: High CLV may chronically favor established segments, leaving growth through new markets or products underserved.
- Over-Targeting Risk: Over-optimizing for short-term yield may harm brand reputation or equity with broader audiences.
Therefore, CLV must be treated with humility—an advanced tool requiring discipline in measurement, calibration, and multi-dimensional insight.
VII. The Influence of Digital Ecosystems
Modern digital ecosystems deliver immense granularity. Every interaction—click, open, referral, session length—is measurable. These dark data provide context for CLV testing, segment behavior, and risk triggers.
However, this scale introduces overfitting risk: spurious correlations may override structural signals. Successful organizations maintain a balance—leveraging high-frequency signals for short-cycle interventions, while retaining medium-term cohort logic for capital allocation and strategic initiatives.
VIII. Ethical and Brand Implications
“CLV”, when viewed through a values lens, also becomes a cultural and ethical marker. Decisions informed by CLV raise questions:
- To what extent should a business monetize a cohort? Is excessive monetization ethical?
- When loyalty programs disproportionately reward high-value customers, does brand equity suffer among moderate spenders?
- When referral bonuses attract opportunists rather than advocates, is brand authenticity compromised?
These considerations demand that CLV strategies incorporate brand and ethical governance, not just financial optimization.
IX. Cross-Functionally Harmonized Governance
A robust operating model to sustain CLV alignment should include:
- Structured Metrics Governance: Common cohort definitions, discount rates, margin allocation, and data timelines maintained under joint sponsorship.
- Integrated Information Architecture: Real-time reporting, defined data lineage (acquisition to LTV), and cross-functional access.
- Quarterly Board Oversight: Board-level dashboards that track digital customer performance and CLV trends as fundamental risk and opportunity signals.
- Ethical Oversight Layer: Cross-functional reviews ensuring CLV-driven decisions don’t undermine customer trust or brand perception.
X. CLV as Strategic Doctrine
When deployed with discipline, CLV becomes more than a metric—it becomes a cultural doctrine. The essential tenets are:
- Time horizon focus: orienting decisions toward lifetime impact rather than short-cycle transactions.
- Cross-functional governance: embedding CLV into finance, marketing, and strategy with shared accountability.
- Continuous recalibration: creating feedback loops that update assumptions and reinforce trust in the metric.
- Ethical stewardship: ensuring customer relationships are respected, brand equity maintained, and monetization balanced.
With that foundation, CLV can guide everything from media budgets and pricing plans to acquisition strategy and market expansion.
Conclusion
In an age where customer relationships define both resilience and revenue, Customer Lifetime Value stands out as an indispensable compass. It unites finance’s need for systematic rigor, marketing’s drive for relevance and engagement, and strategy’s mandate for long-term value creation. When properly modeled, governed, and governed ethically, CLV enables teams to shift from transactional quarterly mindsets to lifetime portfolios—transforming customers into true franchise assets.
For any organization aspiring to mature its performance, CLV is the next frontier. Not just a metric on a dashboard—but a strategic mechanism capable of aligning functions, informing capital allocation, shaping product trajectories, elevating brand meaning, and forging relationships that transcend a single transaction.
Term Sheets: Landmines and Ticking Time Bombs!
Wall Street is the only place that people ride to in a Rolls Royce to get advice from those who take the subway. – Warren Buffett
So the big day is here. You have evangelized your product across various circles and the good news is that a VC has stepped forward to invest in your company. So the hard work is all done! You can rest on your laurels, sign the term sheet that the VC has pushed across the table, and execute the sheet, trigger the stock purchase, voter and investor rights agreements, get the wire and you are up and running! Wait … sounds too good to be true, doesn’t it? And yes you are right! If only things were that easy. The devil is in the details. So let us go over some of the details that you need to watch out for.
1. First, term sheet does not trigger the wire. Signing a term sheet does not mean that the VC will invest in your company. The road is still long and treacherous. All the term sheet does is that it requires you to keep silent on the negotiations, and may even prevent you to shop the deal to anyone else. The key investment terms are laid out in the sheet and would be used in much greater detail when the stock purchase agreement, the investor rights agreement, the voting agreement and other documents are crafted.
 2. Make sure that you have an attorney representing you. And more importantly, an attorney that has experience in the field and has reviewed a lot of such documents. As noted, the devil is in the details. A little “and” or “or” can put you back significantly. But it is just as important for you to know some of the key elements that govern an investment agreement. You can quiz your attorney on these because some of these are important enough to impact your operating degree of freedom in the company.The starting point of a term sheet is valuation of the company. You will hear the concept of pre-money valuation vs. post-money valuation. It is quite simple. The Pre-Money Valuation + Investment = Post-Money Valuation. In other words, Pre-money valuation refers to the value of a company not including external funding or the latest round of funding. Post-Money thus includes the pre-money plus the incremental injection of capital. Let us look at an example:
2. Make sure that you have an attorney representing you. And more importantly, an attorney that has experience in the field and has reviewed a lot of such documents. As noted, the devil is in the details. A little “and” or “or” can put you back significantly. But it is just as important for you to know some of the key elements that govern an investment agreement. You can quiz your attorney on these because some of these are important enough to impact your operating degree of freedom in the company.The starting point of a term sheet is valuation of the company. You will hear the concept of pre-money valuation vs. post-money valuation. It is quite simple. The Pre-Money Valuation + Investment = Post-Money Valuation. In other words, Pre-money valuation refers to the value of a company not including external funding or the latest round of funding. Post-Money thus includes the pre-money plus the incremental injection of capital. Let us look at an example:
Let’s explain the difference by using an example. Suppose that an investor is looking to invest in a start up. Both parties agree that the company is worth $1 million and the investor will put in $250,000.
The ownership percentages will depend on whether this is a $1 million pre-money or post-money valuation. If the $1 million valuation is pre-money, the company is valued at $1 million before the investment and after investment will be valued at $1.25 million. If the $1 million valuation takes into consideration the $250,000 investment, it is referred to as post-money. Thus in a pre-money valuation, the Investor owns 20%. Why? The total valuation is $1.25M which is $1M pre-money + $250K capital. So the math translates to $250K/$1,250K = 20%. If the investor says that they will value company $1M post-money, what they are saying is that they are actually giving you a pre-money valuation of $750K. In other words, they will own 25% of the company rather than 20%. Your ownership rights go down by 5% which, for all intents and purposes, is significant.
3. When a round of financing is done, security is exchanged in lieu of cash received. You already have common stock but these are not the securities being exchanged. The company would issue preferred stock. Preferred stock comes with certain rights, preferences, privileges and covenants. Compared to common stock, it is a superior security. There are a number of important rights and privileges that investors secure via a preferred stock purchase, including a right to a board seat, information rights, a right to participate in future rounds to protect their ownership percentage (called a pro-rata right), a right to purchase any common stock that might come onto the market (called a right of first refusal), a right to participate alongside any common stock that might get sold (called a co-sale right), and an adjustment in the purchase price to reflect sales of stock at lower prices (called an anti-dilution right). Let us examine this in greater detail now. There are two types of preferred. The regular vanilla Convertible Preferred and the Participating Preferred. As the latter name suggests, the Participating Preferred allows the VC to receive back their invested capital and the cumulative dividends, if any before common stockholders (that is you), but also enables them to participate on an as-converted basis in the returns to you, the common stockholder. Here is the math:Let us say company raises $3M at a $3M pre-money valuation. As mentioned before in point (3), the stake is 50%-50% owner-investor.
Let us say company sells for $25M. Now the investor has participating preferred or convertible preferred. How does the difference impact you, the stockholder or the founder. Here goes!
i. Participating Preferred. Investor gets their $3M back. There is still $22M left in the coffers. Investor splits 50-50 based on their participating preferred. You and Investor both take home $11M from the residual pool. Investor has $14M, and you have $11M. Congrats!
ii. Convertible Preferred. Investor gets 50% or $12.5M and you get the same – $12.5M. In other words, convertible preferred just got you a few more drinks at the bar. Hearty Congratulations!
Bear in mind that if the Exit Value is lower, the difference becomes more meaningful. Let us say exit was $10M. The Preferred participant gets $3M + $3.5M = $6.5M while you end up with $3.5M.
 4. One of the key provisions is Liquidation Preferences. It can be a ticking time bomb. Careful! Some investors may sometimes ask for a multiple of their investment as a preference. This provision provides downside protection to investors. In the event of liquidation, the company has to pay back the capital injected for preferred. This would mean a 1X liquidation preference. However, you can have a 2X liquidation preference which means the investor will get back twice as much as what they injected. Most liquidation preferences range from 1X to 2X, although you can have higher liquidation preference multiples as well. However, bear in mind that this becomes important only when the company is forced to liquidate and sell of their assets. If all is gung-ho, this is a silent clause and no sweat off your brow.
4. One of the key provisions is Liquidation Preferences. It can be a ticking time bomb. Careful! Some investors may sometimes ask for a multiple of their investment as a preference. This provision provides downside protection to investors. In the event of liquidation, the company has to pay back the capital injected for preferred. This would mean a 1X liquidation preference. However, you can have a 2X liquidation preference which means the investor will get back twice as much as what they injected. Most liquidation preferences range from 1X to 2X, although you can have higher liquidation preference multiples as well. However, bear in mind that this becomes important only when the company is forced to liquidate and sell of their assets. If all is gung-ho, this is a silent clause and no sweat off your brow.
5. Redemption rights. The right of redemption is the right to demand under certain conditions that the company buys back its own shares from its investors at a fixed price. This right may be included to require a company to buy back its shares if there has not been an exit within a pre-determined period. Failure to redeem shares when requested might result in the investors gaining improved rights, such as enhanced voting rights.
6. The terms could demand that a certain option pool or a pot of stock is kept aside for existing and future employees, or other service providers. It could be a range anywhere between 10-20% of the total stock. When you reserve this pool, you are cutting into your ownership stake. In those instances when you have series of financings and each financing requires you to set aside a small pool, it dilutes you and your previous investors. In general, the way these pools are structured is to give you some headroom up to at least 24 months to accommodate employee growth and providing them incentives. The pool only becomes smaller with the passage of time.
7. Another term is the Anti-Dilution Provision. In its simplest form, anti-dilution rights are a zero- sum game. No one has an advantage over the other. However, this becomes important only when there is a down round. A down round basically means that the company is valued lower in subsequent financing than previously. A company valued at $25M in Series A and $15M in Series B – the Series B would be considered a down round. Two Types of Anti-Dilution:
Full ratchet Anti-Dilution: If the new stock is priced lower than prior stock, the early investor has a clause to convert their shares to the new price. For example, if prior investor paid $1.00 and then it was reset in a later round to $0.50, then the prior investors will have 2X rights to common stock. In other words, you are hit with major dilution as are the later investors. This clause is a big hurdle for new investors.
Weighted Average Anti-Dilution. Old investor’s share is adjusted in proportion to the dilution impact of a down round
8. Pay to Play. These are clauses that work in your, the Company, favor. Basically, investors have to invest some money in later financings, and if they do not – their rights may be reduced. However, having these clauses may put your mind at ease, but may create problems in terms of syndicating or getting investments. Some investors are reluctant to put their money in when there are pay to play clauses in the agreement.
9. Right of First Refusal. A company has no obligation to sell stock in future financing rounds to existing investors. Some investors would like to participate and may seek pro-rata participating to keep their ownership stake the same post-financing. Some investors may even want super pro-rata rights which means that they be allowed to participate to such an extent that their new ownership in the company is greater than their previous ownership stake.
10. Board of Directors. A large board creates complexity. Preferable to have a small but strategic board. New investors will require some representation. If too many investors request representation, the Company may have smaller internal representatives and may be outvoted on certain issues. Be aware of the dynamics of a mushrooming board!
11.Voting Rights. Investors may request certain veto authority or have rights to vote in favor of or against a corporate initiative. Company founders may want super-voting rights to exercise greater control. These matters are delicate and going one way or the other may cause personal issues among the participants. However, these matters can be easily resolved by essentially having carve-outs that spell out rights and encumbrances.
12.Drag Along Provision. Might create an obligation on all shareholders of the company to sell their shares to a potential purchaser if a certain percentage of the shareholders (or of a specific class of shareholders) votes to sell to that purchaser. Often in early rounds drag along rights can only be enforced with the consent of those holding at least a majority of the shares held by investors. These rights can be useful in the context of a sale where potential purchasers will want to acquire 100% of the shares of the company in order to avoid having responsibilities to minority shareholders after the acquisition. Many jurisdictions provide for such a process, usually when a third party has acquired at least 90% of the shares.
13.Representations and Warranties. Venture capital investors expect appropriate representations and warranties to be provided by key founders, management and the company. The primary purpose of the representations and warranties is to provide the investors with a complete and accurate understanding of the current condition of the company and its past history so that the investors can evaluate the risks of investing in the company prior to subscribing for their shares. The representations and warranties will typically cover areas such as the legal existence of the company (including all share capital details), the company’s financial statements, the business plan, asset ownership (in particular intellectual property rights), liabilities (contingent or otherwise), material contracts, employees and litigation. It is very rare that a company is in a perfect state. The warrantors have the opportunity to set out issues which ought to be brought to the attention of the new investors through a disclosure letter or schedule of exceptions. This is usually provided by the warrantors and discloses detailed information concerning any exceptions to or carve-outs from the representations and warranties. If a matter is referred to in the disclosure letter the investors are deemed to have notice of it and will not be able to claim for breach of warranty in respect of that matter. Investors expect those providing representations and warranties about the company to reimburse the investors for the diminution in share value attributable to the representations and warranties being inaccurate or if there are exceptions to them that have not been fully disclosed. There are usually limits to the exposure of the warrantors (i.e. a dollar cap on the amount that can be recovered from individual warrantors). These are matters for negotiation when documentation is being finalized. The limits may vary according to the severity of the breach, the size of the investment and the financial resources of the warrantors. The limits which typically apply to founders are lower than for the company itself (where the company limit will typically be the sum invested or that sum plus a minimum return).
14. Information Rights. In order for venture capital investors to monitor the condition of their investment, it is essential that the company provides them with certain regular updates concerning its financial condition and budgets, as well as a general right to visit the company and examine its books and records. This sometimes includes direct access to the company’s auditors and bankers. These contractually defined obligations typically include timely transmittal of annual financial statements (including audit requirements, if applicable), annual budgets, and audited monthly and quarterly financial statements.
15. Exit. Venture capital investors want to see a path from their investment in the company leading to an exit, most often in the form of a disposal of their shares following an IPO or by participating in a sale. Sometimes the threshold for a liquidity event or will be a qualified exit. If used, it will mean that a liquidity event will only occur, and conversion of preferred shares will only be compulsory, if an IPO falls within the definition of a qualified exit. A qualified exit is usually defined as a sale or IPO on a recognized investment exchange which, in either case, is of a certain value to ensure the investors get a minimum return on their investment. Consequently, investors usually require undertakings from the company and other shareholders that they will endeavor to achieve an appropriate share listing or trade sale within a limited period of time (typically anywhere between 3 and 7 years depending on the stage of investment and the maturity of the company). If such an exit is not achieved, investors often build in structures which will allow them to withdraw some or the entire amount of their investment.
16. Non-Compete, Confidentiality Agreements. It is good practice for any company to have certain types of agreements in place with its employees. For technology start-ups, these generally include Confidentiality Agreements (to protect against loss of company trade secrets, know-how, customer lists, and other potentially sensitive information), Intellectual Property Assignment Agreements (to ensure that intellectual property developed by academic institutions or by employees before they were employed by the company will belong to the company) and Employment Contracts or Consultancy Agreements (which will include provisions to ensure that all intellectual property developed by a company’s employees belongs to the company). Where the company is a spin-out from an academic institution, the founders will frequently be consultants of the company and continue to be employees of the academic institution, at least until the company is more established. Investors also seek to have key founders and managers enter into Non-compete Agreements with the company. In most cases, the investment in the company is based largely on the value of the technology and management experience of the management team and founders. If they were to leave the company to create or work for a competitor, this could significantly affect the company’s value. Investors normally require that these agreements be included in the Investment Agreement as well as in the Employment/Consultancy Agreements with the founders and senior managers, to enable them to have a right of direct action against the founders’ and managers if the restrictions are breached.
Risk Management and Finance
If you are in finance, you are a risk manager. Say what? Risk management! Imagine being the hub in a spoke of functional areas, each of which is embedded with a risk pattern that can vary over time. A sound finance manager would be someone who would be best able to keep pulse, and be able to support the decisions that can contain the risk. Thus, value management becomes critical: Weighing the consequence of a decision against the risk that the decision poses. Not cost management, but value management. And to make value management more concrete, we turn to cash impact or rather – the discounted value of future stream of cash that may or may not be a consequent to a decision. Companies carry risks. If not, a company will not offer any premiums in value to the market. They create competitive advantage – defined as sorting a sustained growth in free cash flow as the key metric that becomes the separator.
John Kay, an eminent strategist, had identified four sources of competitive advantage: Organization Architecture and Culture, Reputation, Innovation and Strategic Assets. All of these are inextricably intertwined, and must be aligned to service value in the company. The business value approach underpins the interrelationships best. And in so doing, scenario planning emerges as a sound machination to manage risks. Understanding the profit impact of a strategy, and the capability/initiative tie-in is one of the most crucial conversations that a good finance manager could encourage in a company. Product, market and internal capabilities become the anchor points in evolving discussions. Scenario planning thus emerges in context of trends and uncertainties: a trend in patterns may open up possibilities, the latter being in the domain of uncertainty.
There are multiple methods one could use in building scenarios and engaging in fruitful risk assessment.
1.Sensitivity Assessment: Evaluate decisions in the context of the strategy’s reliance on the resilience of business conditions. Assess the various conditions in a scenario or mutually exclusive scenarios, assess a probabilistic guesstimate on success factors, and then offer simple solutions. This assessment tends to be heuristic oriented and excellent when one is dealing with few specific decisions to be made. There is an elevated sense of clarity with regard to the business conditions that may present itself. And this is most commonly used, but does not thwart the more realistic conditions where clarity is obfuscated and muddy.
2.Strategy Evaluation: Use scenarios to test a strategy by throwing a layer of interaction complexity. To the extent you can disaggregate the complexity, the evaluation of a strategy is better tenable. But once again, disaggregation has its downsides. We don’t operate in a vacuum. It is the aggregation, and negotiating through this aggregation effectively is where the real value is. You may have heard of the Mckinsey MECE (Mutually Exclusive; Comprehensively Exhaustive) methodology where strategic thrusts are disaggregated and contained within a narrow framework. The idea is that if one does that enough, one has an untrammeled confidence in choosing one initiative over another. That is true again in some cases, but my belief is that the world operates at a more synthetic level than pure analytic. We resort to analytics since it is too damned hard to synthesize, and be able to agree on an optimal solution. I am not creaming analytics; I am only suggesting that there is some possibility that a false hypothesis is accepted and a true one rejected. Thus analytics is an important tool, but must be weighed along with the synthetic tradition.
3.Synthetic Development: By far the most interesting and perhaps the most controversial with glint of academic and theoretical monstrosities included – this represents developing and broadcasting all scenarios equally weighed, and grouping interaction of scenarios. Thus, if introducing a multi-million dollar initiative in untested waters is a decision you have to weigh, one must go through the first two methods, and then review the final outcome against peripheral factors that were not introduced initially. A simple statement or realization like – The competition for Southwest is the Greyhound bus – could significantly alter the expanse of the strategy.
If you think of the new world of finance being nothing more than crunching numbers … stop and think again. Yes …crunching those numbers play a big part, less a cause than an effect of the mental model that you appropriate in this prized profession.