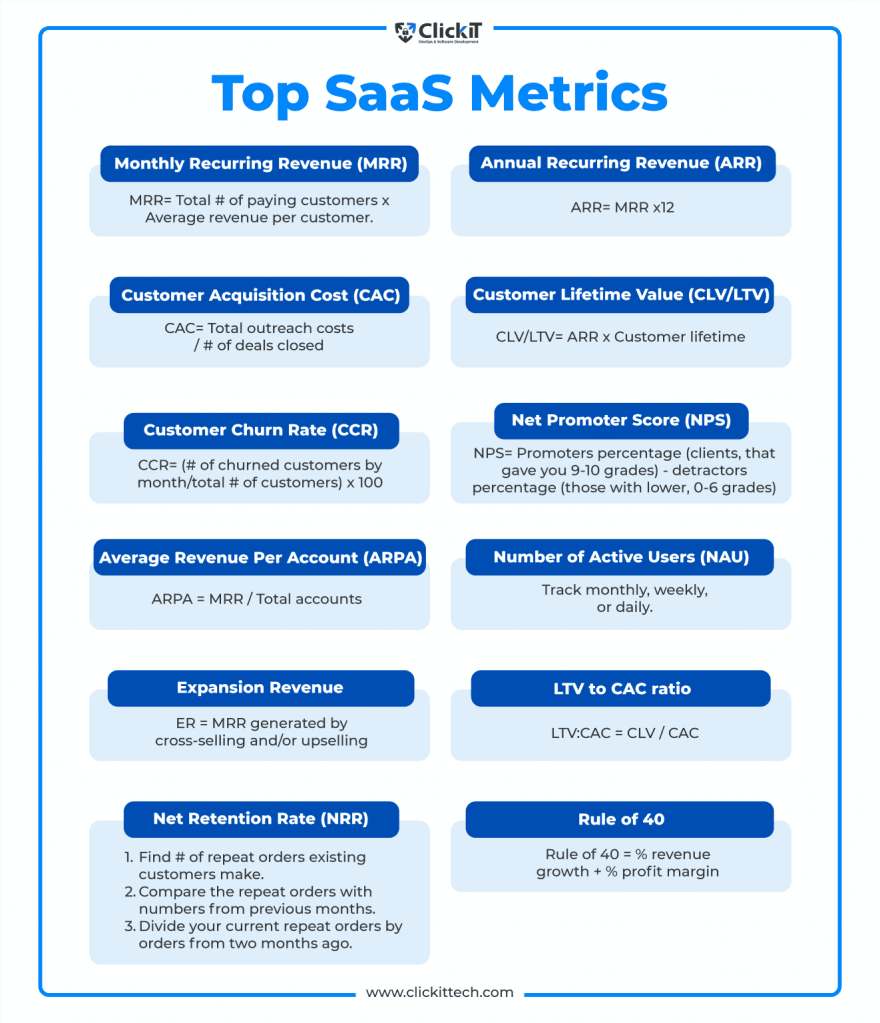
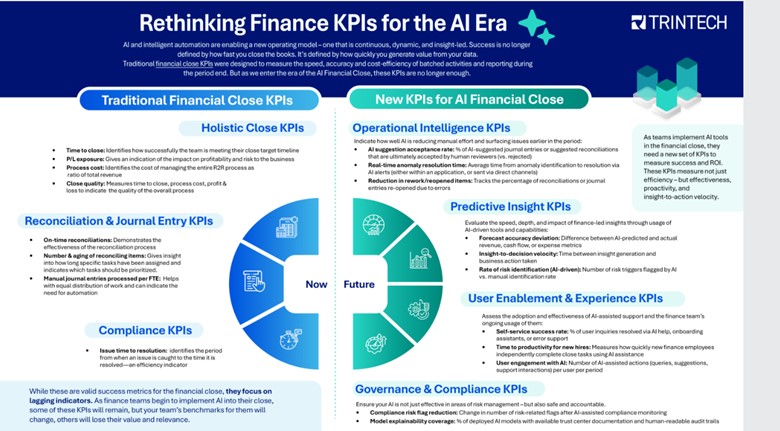
Blog Archives
The CFO as Chief Option Architect: Embracing Uncertainty
Part I: Embracing the Options Mindset
This first half explores the philosophical and practical foundation of real options thinking, scenario-based planning, and the CFO’s evolving role in navigating complexity. The voice is grounded in experience, built on systems thinking, and infused with a deep respect for the unpredictability of business life.
I learned early that finance, for all its formulas and rigor, rarely rewards control. In one of my earliest roles, I designed a seemingly watertight budget, complete with perfectly reconciled assumptions and cash flow projections. The spreadsheet sang. The market didn’t. A key customer delayed a renewal. A regulatory shift in a foreign jurisdiction quietly unraveled a tax credit. In just six weeks, our pristine model looked obsolete. I still remember staring at the same Excel sheet and realizing that the budget was not a map, but a photograph, already out of date. That moment shaped much of how I came to see my role as a CFO. Not as controller-in-chief, but as architect of adaptive choices.

The world has only become more uncertain since. Revenue operations now sit squarely in the storm path of volatility. Between shifting buying cycles, hybrid GTM models, and global macro noise, what used to be predictable has become probabilistic. Forecasting a quarter now feels less like plotting points on a trendline and more like tracing potential paths through fog. It is in this context that I began adopting and later, championing, the role of the CFO as “Chief Option Architect.” Because when prediction fails, design must take over.
This mindset draws deeply from systems thinking. In complex systems, what matters is not control, but structure. A system that adapts will outperform one that resists. And the best way to structure flexibility, I have found, is through the lens of real options. Borrowed from financial theory, real options describe the value of maintaining flexibility under uncertainty. Instead of forcing an all-in decision today, you make a series of smaller decisions, each one preserving the right, but not the obligation, to act in a future state. This concept, though rooted in asset pricing, holds powerful relevance for how we run companies.
When I began modeling capital deployment for new GTM motions, I stopped thinking in terms of “budget now, or not at all.” Instead, I started building scenario trees. Each branch represented a choice: deploy full headcount at launch or split into a two-phase pilot with a learning checkpoint. Invest in a new product SKU with full marketing spend, or wait for usage threshold signals to pass before escalation. These decision trees capture something that most budgets never do—the reality of the paths not taken, the contingencies we rarely discuss. And most importantly, they made us better at allocating not just capital, but attention. I am sharing my Bible on this topic, which was referred to me by Dr. Alexander Cassuto at Cal State Hayward in the Econometrics course. It was definitely more pleasant and easier to read than Jiang’s book on Econometrics.

This change in framing altered my approach to every part of revenue operations. Take, for instance, the deal desk. In traditional settings, deal desk is a compliance checkpoint where pricing, terms, and margin constraints are reviewed. But when viewed through an options lens, the deal desk becomes a staging ground for strategic bets. A deeply discounted deal might seem reckless on paper, but if structured with expansion clauses, usage gates, or future upsell options, it can behave like a call option on account growth. The key is to recognize and price the option value. Once I began modeling deals this way, I found we were saying “yes” more often, and with far better clarity on risk.
Data analytics became essential here not for forecasting the exact outcome, but for simulating plausible ones. I leaned heavily on regression modeling, time-series decomposition, and agent-based simulation. We used R to create time-based churn scenarios across customer cohorts. We used Arena to simulate resource allocation under delayed expansion assumptions. These were not predictions. They were controlled chaos exercises, designed to show what could happen, not what would. But the power of this was not just in the results, but it was in the mindset it built. We stopped asking, “What will happen?” and started asking, “What could we do if it does?”
From these simulations, we developed internal thresholds to trigger further investment. For example, if three out of five expansion triggers were fired, such as usage spike, NPS improvement, and additional department adoption, then we would greenlight phase two of GTM spend. That logic replaced endless debate with a predefined structure. It also gave our board more confidence. Rather than asking them to bless a single future, we offered a roadmap of choices, each with its own decision gates. They didn’t need to believe our base case. They only needed to believe we had options.
Yet, as elegant as these models were, the most difficult challenge remained human. People, understandably, want certainty. They want confidence in forecasts, commitment to plans, and clarity in messaging. I had to coach my team and myself to get comfortable with the discomfort of ambiguity. I invoked the concept of bounded rationality from decision science: we make the best decisions we can with the information available to us, within the time allotted. There is no perfect foresight. There is only better framing.
This is where the law of unintended consequences makes its entrance. In traditional finance functions, overplanning often leads to rigidity. You commit to hiring plans that no longer make sense three months in. You promise CAC thresholds that collapse under macro pressure. You bake linearity into a market that moves in waves. When this happens, companies double down, pushing harder against the wrong wall. But when you think in options, you pull back when the signal tells you to. You course-correct. You adapt. And paradoxically, you appear more stable.
As we embedded this thinking deeper into our revenue operations, we also became more cross-functional. Sales began to understand the value of deferring certain go-to-market investments until usage signals validated demand. Product began to view feature development as portfolio choices: some high-risk, high-return, others safer but with less upside. Customer Success began surfacing renewal and expansion probabilities not as binary yes/no forecasts, but as weighted signals on a decision curve. The shared vocabulary of real options gave us a language for navigating ambiguity together.
We also brought this into our capital allocation rhythm. Instead of annual budget cycles, we moved to rolling forecasts with embedded thresholds. If churn stayed below 8% and expansion held steady, we would greenlight an additional five SDRs. If product-led growth signals in EMEA hit critical mass, we’d fund a localized support pod. These weren’t whims. They were contingent commitments, bound by logic, not inertia. And that changed everything.
The results were not perfect. We made wrong bets. Some options expired worthless. Others took longer to mature than we expected. But overall, we made faster decisions with greater alignment. We used our capital more efficiently. And most of all, we built a culture that didn’t flinch at uncertainty—but designed for it.
In the next part of this essay, I will go deeper into the mechanics of implementing this philosophy across the deal desk, QTC architecture, and pipeline forecasting. I will also show how to build dashboards that visualize decision trees and option paths, and how to teach your teams to reason probabilistically without losing speed. Because in a world where volatility is the only certainty, the CFO’s most enduring edge is not control, but it is optionality, structured by design and deployed with discipline.
Part II: Implementing Option Architecture Inside RevOps
A CFO cannot simply preach agility from a whiteboard. To embed optionality into the operational fabric of a company, the theory must show up in tools, in dashboards, in planning cadences, and in the daily decisions made by deal desks, revenue teams, and systems owners. I have found that fundamental transformation comes not from frameworks, but from friction—the friction of trying to make the idea work across functions, under pressure, and at scale. That’s where option thinking proves its worth.
We began by reimagining the deal desk, not as a compliance stop but as a structured betting table. In conventional models, deal desks enforce pricing integrity, review payment terms, and ensure T’s and C’s fall within approved tolerances. That’s necessary, but not sufficient. In uncertain environments—where customer buying behavior, competitive pressure, or adoption curves wobble without warning: rigid deal policies become brittle. The opportunity lies in recasting the deal desk as a decision node within a larger options tree.
Consider a SaaS enterprise deal involving land-and-expand potential. A rigid model forces either full commitment upfront or defers expansion, hoping for a vague “later.” But if we treat the deal like a compound call option, we see more apparent logic. You price the initial land deal aggressively, with usage-based triggers that, when met, unlock favorable expansion terms. You embed a re-pricing clause if usage crosses a defined threshold in 90 days. You insert a “soft commit” expansion clause tied to the active user count. None of these is just a term. They are embedded with real options. And when structured well, they deliver upside without requiring the customer to commit to uncertain future needs.
In practice, this approach meant reworking CPQ systems, retraining legal, and coaching reps to frame options credibly. We designed templates with optionality clauses already coded into Salesforce workflows. Once an account crossed a pre-defined trigger say, 80% license utilization, then the next best action flowed to the account executive and customer success manager. The logic wasn’t linear. It was branching. We visualized deal paths in a way that corresponds to mapping a decision tree in a risk-adjusted capital model.
Yet even the most elegant structure can fail if the operating rhythm stays linear. That is why we transitioned away from rigid quarterly forecasts toward rolling scenario-based planning. Forecasting ceased to be a spreadsheet contest. Instead, we evaluated forecast bands, not point estimates. If base churn exceeded X% in a specific cohort, how did that impact our expansion coverage ratio? If deal velocity in EMEA slowed by two weeks, how would that compress the bookings-to-billings gap? We visualized these as cascading outcomes, not just isolated misses.
To build this capability, we used what I came to call “option dashboards.” These were layered, interactive models with inputs tied to a live pipeline and post-sale telemetry. Each card on the dashboard represented a decision node—an inflection point. Would we deploy more headcount into SMB if the average CAC-to-LTV fell below 3:1? Would we pause feature rollout in one region to redirect support toward a segment with stronger usage signals? Each choice was pre-wired with boundary logic. The decisions didn’t live in a drawer—they lived in motion.
Building these dashboards required investment. But more than tools, it required permission. Teams needed to know they could act on signal, not wait for executive validation every time a deviation emerged. We institutionalized the language of “early signal actionability.” If revenue leaders spotted a decline in renewal health across a cluster of customers tied to the same integration module, they didn’t wait for a churn event. They pulled forward roadmap fixes. That wasn’t just good customer service, but it was real options in flight.
This also brought a new flavor to our capital allocation rhythm. Rather than annual planning cycles that locked resources into static swim lanes, we adopted gated resourcing tied to defined thresholds. Our FP&A team built simulation models in Python and R, forecasting the expected value of a resourcing move based on scenario weightings. For example, if a new vertical showed a 60% likelihood of crossing a 10-deal threshold by mid-Q3, we pre-approved GTM spend to activate contingent on hitting that signal. This looked cautious to some. But in reality, it was aggressive and in the right direction, at the right moment.
Throughout all of this, I kept returning to a central truth: uncertainty punishes rigidity, but rewards those who respect its contours. A pricing policy that cannot flex will leave margin on the table or kill deals in flight. A hiring plan that commits too early will choke working capital. And a CFO who waits for clarity before making bets will find they arrive too late. In decision theory, we often talk about “the cost of delay” versus “the cost of error.” A good options model minimizes both, which, interestingly, is not by being just right, but by being ready.
Of course, optionality without discipline can devolve into indecision. We embedded guardrails. We defined thresholds that made decision inertia unacceptable. If a cohort’s NRR dropped for three consecutive months and win-back campaigns failed, we sunsetted that motion. If a beta feature was unable to hit usage velocity within a quarter, we reallocated the development budget. These were not emotional decisions, but they were logical conclusions of failed options. And we celebrated them. A failed option, tested and closed, beats a zombie investment every time.
We also revised our communication with the board. Instead of defending fixed forecasts, we presented probability-weighted trees. “If churn holds, and expansion triggers fire, we’ll beat target by X.” “If macro shifts pull SMB renewals down by 5%, we stay within plan by flexing mid-market initiatives.” This shifted the conversation from finger-pointing to scenario readiness. Investors liked it. More importantly, so did the executive team. We could disagree on base assumptions but still align on decisions because we’d mapped the branches ahead of time.
One area where this thought made an outsized impact was compensation planning. Sales comp is notoriously fragile under volatility. We redesigned quota targets and commission accelerators using scenario bands, not fixed assumptions. We tested payout curves under best, base, and downside cases. We then ran Monte Carlo simulations to see how frequently actuals would fall into the “too much upside” or “demotivating downside” zones. This led to more durable comp plans, which meant fewer panicked mid-year resets. Our reps trusted the system. And our CFO team could model cost predictability with far greater confidence.
In retrospection, all these loops back to a single mindset shift: you don’t plan to be right. You plan to stay in the game. And staying in the game requires options that are well-designed, embedded into the process, and respected by every function. Sales needs to know they can escalate an expansion offer once particular customer signals fire. Success needs to know they have the budget authority to engage support when early churn flags arise. Product needs to know they can pause a roadmap stream if NPV no longer justifies it. And finance needs to know that its most significant power is not in control, but in preparation.
Today, when I walk into a revenue operations review or a strategic planning offsite, I do not bring a budget with fixed forecasts. I get a map. It has branches. It has signals. It has gates. And it has options, and each one designed not to predict the future, but to help us meet it with composure, and to move quickly when the fog clears.
Because in the world I have operated in, spanning economic cycles, geopolitical events, sudden buyer hesitation, system failures, and moments of exponential product success since 1994 until now, one principle has held. The companies that win are not the ones who guess right. They are the ones who remain ready. And readiness, I have learned, is the true hallmark of a great CFO.
Precision at Scale: How to Grow Without Drowning in Complexity
In business, as in life, scale is seductive. It promises more of the good things—revenue, reach, relevance. But it also invites something less welcome: complexity. And the thing about complexity is that it doesn’t ask for permission before showing up. It simply arrives, unannounced, and tends to stay longer than you’d like.
As we pursue scale, whether by growing teams, expanding into new markets, or launching adjacent product lines, we must ask a question that seems deceptively simple: how do we know we’re scaling the right way? That question is not just philosophical—it’s deeply economic. The right kind of scale brings leverage. The wrong kind brings entropy.

Now, if I’ve learned anything from years of allocating capital, it is this: returns come not just from growth, but from managing the cost and coordination required to sustain that growth. In fact, the most successful enterprises I’ve seen are not the ones that scaled fastest. They’re the ones that scaled precisely. So, let’s get into how one can scale thoughtfully, without overinvesting in capacity, and how to tell when the system you’ve built is either flourishing or faltering.
To begin, one must understand that scale and complexity do not rise in parallel; complexity has a nasty habit of accelerating. A company with two teams might have a handful of communication lines. Add a third team, and you don’t just add more conversations—you add relationships between every new and existing piece. In engineering terms, it’s a combinatorial explosion. In business terms, it’s meetings, misalignment, and missed expectations.
Cities provide a useful analogy. When they grow in population, certain efficiencies appear. Infrastructure per person often decreases, creating cost advantages. But cities also face nonlinear rises in crime, traffic, and disease—all manifestations of unmanaged complexity. The same is true in organizations. The system pays a tax for every additional node, whether that’s a service, a process, or a person. That tax is complexity, and it compounds.
Knowing this, we must invest in capacity like we would invest in capital markets—with restraint and foresight. Most failures in capacity planning stem from either a lack of preparation or an excess of confidence. The goal is to invest not when systems are already breaking, but just before the cracks form. And crucially, to invest no more than necessary to avoid those cracks.
Now, how do we avoid overshooting? I’ve found that the best approach is to treat capacity like runway. You want enough of it to support takeoff, but not so much that you’ve spent your fuel on unused pavement. We achieve this by investing in increments, triggered by observable thresholds. These thresholds should be quantitative and predictive—not merely anecdotal. If your servers are running at 85 percent utilization across sustained peak windows, that might justify additional infrastructure. If your engineering lead time starts rising despite team growth, it suggests friction has entered the system. Either way, what you’re watching for is not growth alone, but whether the system continues to behave elegantly under that growth.
Elegance matters. Systems that age well are modular, not monolithic. In software, this might mean microservices that scale independently. In operations, it might mean regional pods that carry their own load, instead of relying on a centralized command. Modular systems permit what I call “selective scaling”—adding capacity where needed, without inflating everything else. It’s like building a house where you can add another bedroom without having to reinforce the foundation. That kind of flexibility is worth gold.
Of course, any good decision needs a reliable forecast behind it. But forecasting is not about nailing the future to a decimal point. It is about bounding uncertainty. When evaluating whether to scale, I prefer forecasts that offer a range—base, best, and worst-case scenarios—and then tie investment decisions to the 75th percentile of demand. This ensures you’re covering plausible upside without betting on the moon.
Let’s not forget, however, that systems are only as good as the signals they emit. I’m wary of organizations that rely solely on lagging indicators like revenue or margin. These are important, but they are often the last to move. Leading indicators—cycle time, error rates, customer friction, engineer throughput—tell you much sooner whether your system is straining. In fact, I would argue that latency, broadly defined, is one of the clearest signs of stress. Latency in delivery. Latency in decisions. Latency in feedback. These are the early whispers before systems start to crack.
To measure whether we’re making good decisions, we need to ask not just if outcomes are improving, but if the effort to achieve them is becoming more predictable. Systems with high variability are harder to scale because they demand constant oversight. That’s a recipe for executive burnout and organizational drift. On the other hand, systems that produce consistent results with declining variance signal that the business is not just growing—it’s maturing.
Still, even the best forecasts and the finest metrics won’t help if you lack the discipline to say no. I’ve often told my teams that the most underrated skill in growth is the ability to stop. Stopping doesn’t mean failure; it means the wisdom to avoid doubling down when the signals aren’t there. This is where board oversight matters. Just as we wouldn’t pour more capital into an underperforming asset without a turn-around plan, we shouldn’t scale systems that aren’t showing clear returns.
So when do we stop? There are a few flags I look for. The first is what I call capacity waste—resources allocated but underused, like a datacenter running at 20 percent utilization, or a support team waiting for tickets that never come. That’s not readiness. That’s idle cost. The second flag is declining quality. If error rates, customer complaints, or rework spike following a scale-up, then your complexity is outpacing your coordination. Third, I pay attention to cognitive load. When decision-making becomes a game of email chains and meeting marathons, it’s time to question whether you’ve created a machine that’s too complicated to steer.
There’s also the budget creep test. If your capacity spending increases by more than 10 percent quarter over quarter without corresponding growth in throughput, you’re not scaling—you’re inflating. And in inflation, as in business, value gets diluted.
One way to guard against this is by treating architectural reserves like financial ones. You wouldn’t deploy your full cash reserve just because an opportunity looks interesting. You’d wait for evidence. Similarly, system buffers should be sized relative to forecast volatility, not organizational ambition. A modest buffer is prudent. An oversized one is expensive insurance.
Some companies fall into the trap of building for the market they hope to serve, not the one they actually have. They build as if the future were guaranteed. But the future rarely offers such certainty. A better strategy is to let the market pull capacity from you. When customers stretch your systems, then you invest. Not because it’s a bet, but because it’s a reaction to real demand.
There’s a final point worth making here. Scaling decisions are not one-time events. They are sequences of bets, each informed by updated evidence. You must remain agile enough to revise the plan. Quarterly evaluations, architectural reviews, and scenario testing are the boardroom equivalent of course correction. Just as pilots adjust mid-flight, companies must recalibrate as assumptions evolve.
To bring this down to earth, let me share a brief story. A fintech platform I advised once found itself growing at 80 percent quarter over quarter. Flush with success, they expanded their server infrastructure by 200 percent in a single quarter. For a while, it worked. But then something odd happened. Performance didn’t improve. Latency rose. Error rates jumped. Why? Because they hadn’t scaled the right parts. The orchestration layer, not the compute layer, was the bottleneck. Their added capacity actually increased system complexity without solving the real issue. It took a re-architecture, and six months of disciplined rework, to get things back on track. The lesson: scaling the wrong node is worse than not scaling at all.
In conclusion, scale is not the enemy. But ungoverned scale is. The real challenge is not growth, but precision. Knowing when to add, where to reinforce, and—perhaps most crucially—when to stop. If we build systems with care, monitor them with discipline, and remain intellectually honest about what’s working, we give ourselves the best chance to grow not just bigger, but better.
And that, to borrow a phrase from capital markets, is how you compound wisely.
Systems Thinking and Complexity Theory: Practical Tools for Complex Business Challenges
In business today, leaders are expected to make decisions faster and with better outcomes, often in environments filled with ambiguity and noise. The difference between companies that merely survive and those that thrive often comes down to the quality of thinking behind those decisions.
Two powerful tools that help elevate decision quality are systems thinking and complexity theory. These approaches are not academic exercises. They are practical ways to better understand the big picture, anticipate unintended consequences, and focus on what truly matters. They help leaders see connections across functions, understand how behavior evolves over time, and adapt more effectively when conditions change.
Let us first understand what each of these ideas means, and then look at how they can be applied to real business problems.
What is Systems Thinking?
Systems thinking is an approach that looks at a problem not in isolation but as part of a larger system of related factors. Rather than solving symptoms, it helps identify root causes. It focuses on how things interact over time, including feedback loops and time delays that may not be immediately obvious.
Imagine you are managing a business and notice that sales conversions are low. A traditional response might be to retrain the sales team or change the pitch deck. A systems thinker would ask broader questions. Are the leads being qualified properly? Has marketing changed its targeting criteria? Is pricing aligned with customer expectations? Are there delays in proposal generation? You begin to realize that what looks like a sales issue could be caused by something upstream in marketing or downstream in operations.
What is Complexity Theory?
Complexity theory applies when a system is made up of many agents or parts that interact and change over time. These parts adapt to one another, and the system as a whole evolves in unpredictable ways. In a complex system, outcomes are not linear. Small inputs can lead to large outcomes, and seemingly stable patterns can suddenly shift.
A good example is employee engagement. You might roll out a well-designed recognition program and expect morale to improve. But in practice, results may vary because employees interpret and respond differently based on team dynamics, trust in leadership, or recent changes in workload. Complexity theory helps leaders approach these systems with humility, awareness, and readiness to adjust based on feedback from the system itself.
Applying These Ideas to Real Business Challenges
Use Case 1: Sales Pipeline Bottleneck
A common challenge in many organizations is a slowdown or bottleneck in the sales pipeline. Traditional metrics may show that qualified leads are entering the top of the funnel, but deals are not progressing. Rather than focusing only on sales performance, a systems thinking approach would involve mapping the full sales cycle.
You might uncover that the product demo process is delayed because of engineering resource constraints. Or perhaps legal review for proposals is taking longer due to new compliance requirements. You may even discover that the leads being passed from marketing do not match the sales team’s target criteria, leading to wasted effort.
Using systems thinking, you start to see that the sales pipeline is not a simple sequence. It is an interconnected system involving marketing, sales, product, legal, and customer success. A change in one part affects the others. Once the feedback loops are visible, solutions become clearer and more effective. This might involve realigning handoff points, adjusting incentive structures, or investing in automation to speed up internal reviews.
In a more complex situation, complexity theory becomes useful. For example, if customer buying behavior has changed due to economic uncertainty, the usual pipeline patterns may no longer apply. You may need to test multiple strategies and watch for how the system responds, such as shortening the sales cycle for certain segments or offering pilot programs. You learn and adjust in real time, rather than assuming a static playbook will work.
Use Case 2: Increase in Voluntary Attrition
Voluntary attrition, especially among high performers, often triggers a reaction from HR to conduct exit interviews or offer retention bonuses. While these steps have some value, they often miss the deeper systemic causes.
A systems thinking approach would examine the broader employee experience. Are new hires receiving proper onboarding? Is workload increasing without changes in staffing? Are team leads trained in people management? Is career development aligned with employee expectations?
You might find that a recent reorganization led to unclear roles, increased stress, and a breakdown in peer collaboration. None of these factors alone might seem critical, but together they form a reinforcing loop that drives disengagement. Once identified, you can target specific leverage points, such as improving communication channels, resetting team norms, or introducing job rotation to restore a sense of progress and purpose.
Now layer in complexity theory. Culture, trust, and morale are not mechanical systems. They evolve based on stories people tell, leadership behavior, and informal networks. The same policy change can be embraced in one part of the organization and resisted in another. Solutions here often involve small interventions and feedback loops. You might launch listening sessions, try lightweight pulse surveys, or pilot flexible work models in select teams. You then monitor the ripple effects. The goal is not full control, but guided adaptation.
Separating Signal from Noise
In both examples above, systems thinking and complexity theory help leaders rise above the noise. Not every metric, complaint, or fluctuation requires action. But when seen in context, some of these patterns reveal early signals of deeper shifts.
The strength of these frameworks is that they encourage patience, curiosity, and structured exploration. You avoid knee-jerk reactions and instead look for root causes and emerging trends. Over time, this leads to better diagnosis, better prioritization, and better outcomes.
Final Thoughts
In a world where data is abundant but insight is rare, systems thinking and complexity theory provide a critical edge. They help organizations become more aware, more adaptive, and more resilient.
Whether you are trying to improve operational efficiency, respond to market changes, or build a healthier culture, these approaches offer practical tools to move from reactive problem-solving to thoughtful system design.
You do not need to be a specialist to apply these principles. You just need to be willing to ask broader questions, look for patterns, and stay open to learning from the system you are trying to improve.
This kind of thinking is not just smart. It is becoming essential for long-term business success.